Table of contents
Video 10 Training and testing 10-20-2021
Outline
- From training to testing
- Illustrative examples
- Break point
- Puzzle
Train multiple model / hypotheses:
$$ \mathbb P[|E_{in} - E_{out}| > \varepsilon] \leq \underbrace{2 \ M \ e^{-2\varepsilon^2 N}}_{\text{union bound}} $$Test one model / hypothesis: (Hoeffding Inequality)
$$ \mathbb P[|E_{in} - E_{out}| > \varepsilon] \leq 2 e^{-2\varepsilon^2 N} $$M: 假设集中所有可能假设的个数, 可以是无穷,所以概率可以是无穷,就不能保证 $E_{out}\approx E_{in}$
Learning is to find the best hypothesis g which make the probability of "" ($\mathcal B$ad event) minimum.
“Learning” 是找到假设集中的最佳假设 g(让 $\mathcal B$ad event: $|E_{in}(h_m) - E_{out}(h_m)|>\varepsilon$ 发生的概率最小),g 可以是假设1,或者假设2,…,或者假设M,就对应概率相加,就是union bound:
$$ \mathbb P [\rm \mathcal B_1 or \mathcal B_2 or \cdots \mathcal B_M] \leq \underbrace{ \mathbb P [\mathcal B_1] + \mathbb P [\mathcal B_2] + \cdots +\mathbb P [\mathcal B_M]}_{\text{no overlaps: M terms}} $$“等于” 发生在它们互不重叠的情况,如果各假设间有重叠,它们的和就变小。
事实上,Bad Events are very overlapping.
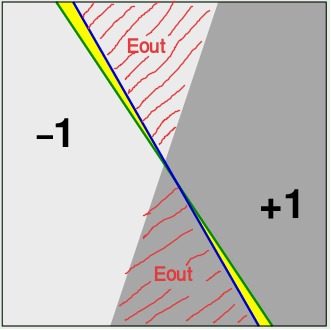
白色与灰色分界线是 unknown target function。 蓝线和绿线是两个 hypothesis。 假设 h 与真实界线所差的面积(红色阴影)是$E_{out}$,黄色面积是 $\Delta E_{out}$。$E_{in}$未在图中体现,需要对整个面积空间采样,样本点落在 $E_{out}$ 中的个数是$E_{in}$,样本点落在黄色区域内的个数是$\Delta E_{in}$。 $h_1$ 与 $h_2$ 有很大的重叠,$|E_{in}(h_1) - E_{out}(h_1)| \approx |E_{in}(h_2)-E_{out}(h_2)|$
改变h,$E_{out}$ 有显著变化,但$E_{in}$不会有显著变化,因为训练集样本点的个数很有限。所以很多假设的分类效果是一样的。
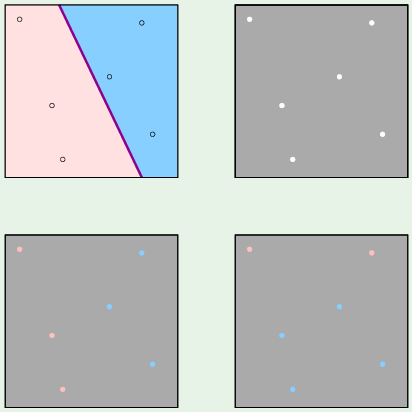
Replace M with the number of dichotomies (把样本点成功二分类的斜线的条数).
A hypothesis $\rightarrow$ A dichotomy
-
A dichotomy is a mini hypothesis
-
对比:
- Input space:
- A hypothesis, 全输入空间都是输入 $h: \mathcal X \rightarrow\{-1, +1\}$
- A dichotomy, 只有 N 个训练点 $h: \{\mathbf{x_1,x_2,\cdots,x_N}\}\rightarrow \{-1, +1\}$
- Number of hypotheses
- $|\mathcal H|$ = M: 可以是无穷个
- $|\mathcal H(\mathbf{x_1,x_2,\cdots,x_N}\})|$ = $m_{\mathcal H}(N)$ 最多 $2^N$ 个 (N个$\pm 1$组合)
- Input space:
-
用 growth function $m_{\mathcal H}(N)$ 替代 M
$m_{\mathcal H}(N)$ 必须是polynomial in N,这样e的负指数可以起作用抵消 $m_{\mathcal H}(N)$,让union bound变得小。
Growth function $m_{\mathcal H} (N)$
-
由 N 个样本点组成任意的,能成功被假设集 $\mathcal H$ 二分的 dichotomies 最多的个数 (不限位置): $m_{\mathcal H}(N) = \underset{x_1,\cdots,x_N \in \mathcal X}{max}\ |\mathcal H(x_1, \cdots, x_N)|$. (“most dichotomies on any N points”)
$$ m_{\mathcal H}(N) \leq 2^N $$ -
有些 config 的 dichotomies 达不到 $2^N$ 种:
-
对于 2D perceptron hypothesis / dichotomies:
-
3个点,最多能分8种(若限定点的位置可能更少)
-
4个点,最多能分14种(有2种情况 (异或),2D perceptron分不开)
(2行2列摆放最多)按照4个o,3个o (1个x),2个o,1个o,0个o 排列组合。
如果4点共线,只能分8种。
如果3点共线,余1个单独在一行,只能分12种。
-
-
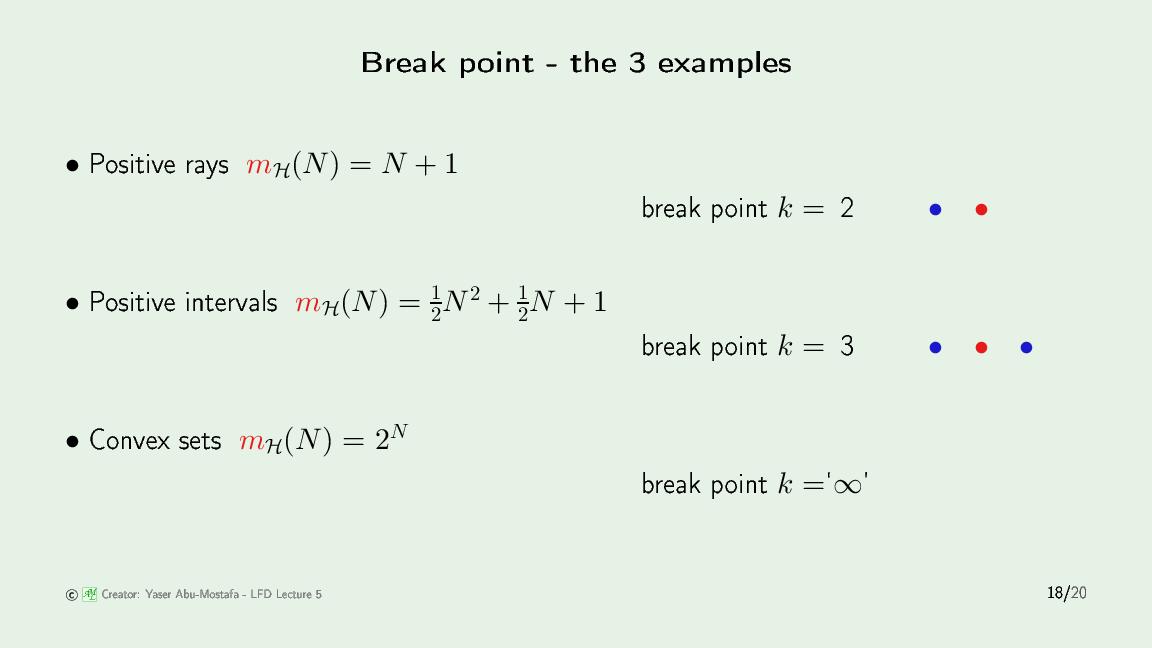
对于 Positive rays hypothesis:
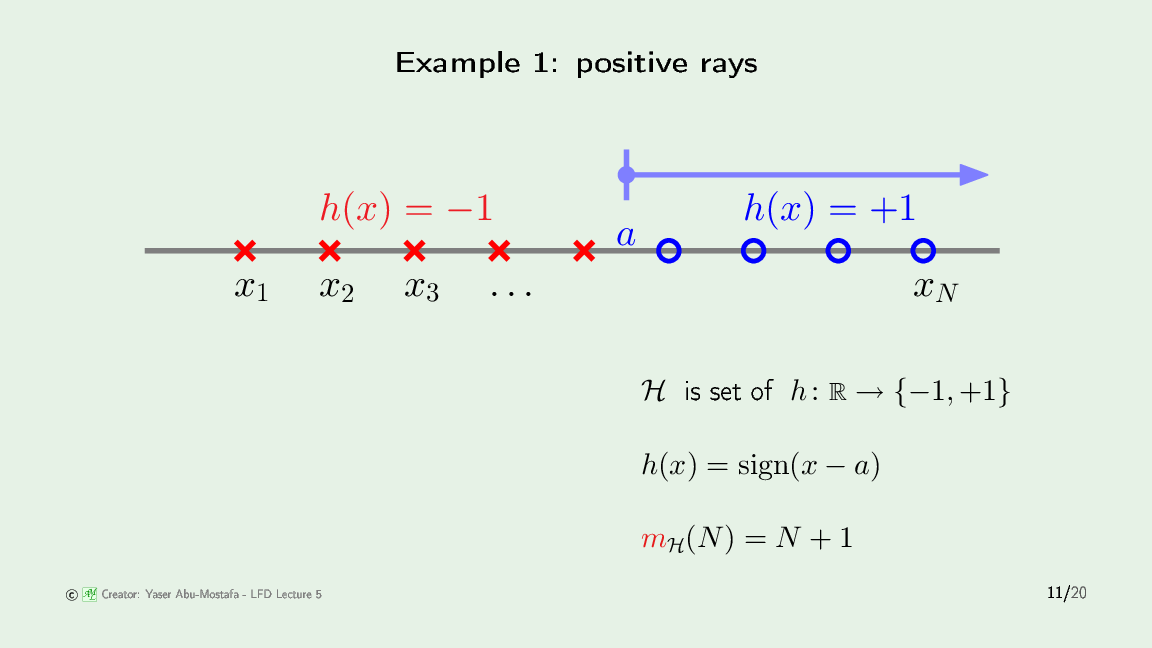
位置摆放是固定的:共线。对于N个点,正射线只能处理 N+1 种配置,也就是圆圈全在右侧,可以是0个圈,1个圈,2个圈,…,N个圈。
-
对于 Positive Intervals hypothesis
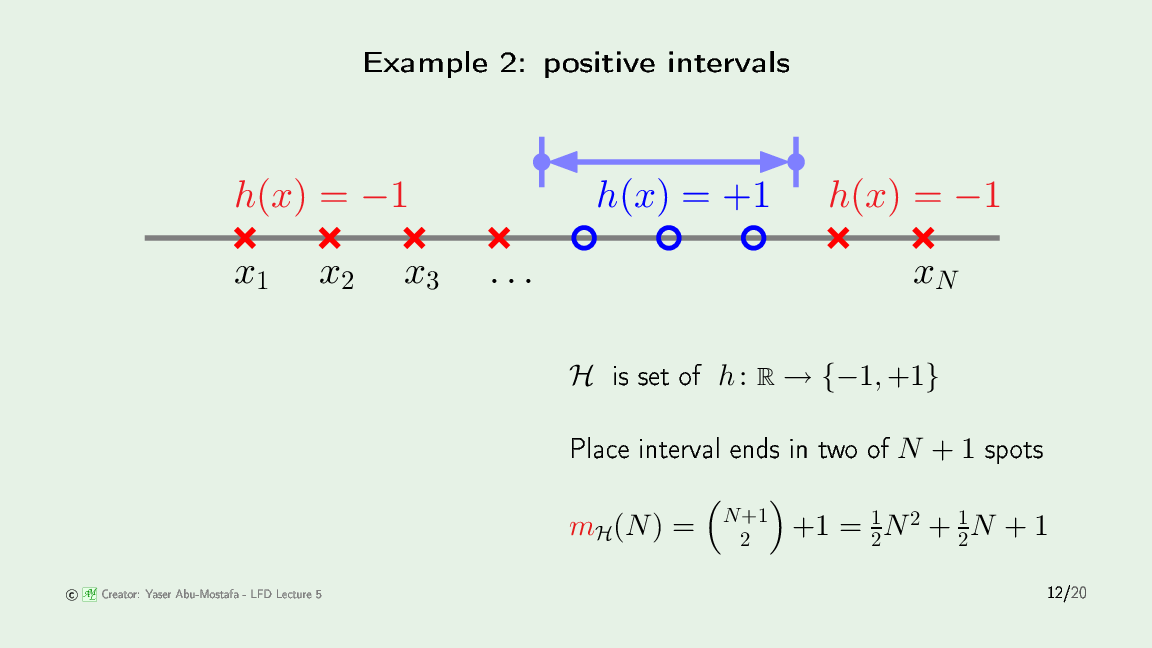
正区间只能处理中间有一段是+1,两侧是-1的配置。需要用两个边界 (threshold) 来确定一个区间:一共有N个点,形成N+1个空,在这N+1个空里选两个,就形成了一个区间,所以是 $C_{N+1}^2$,再加上两个边界在同一个空的情况。
-
对于 Convex sets hypothesis
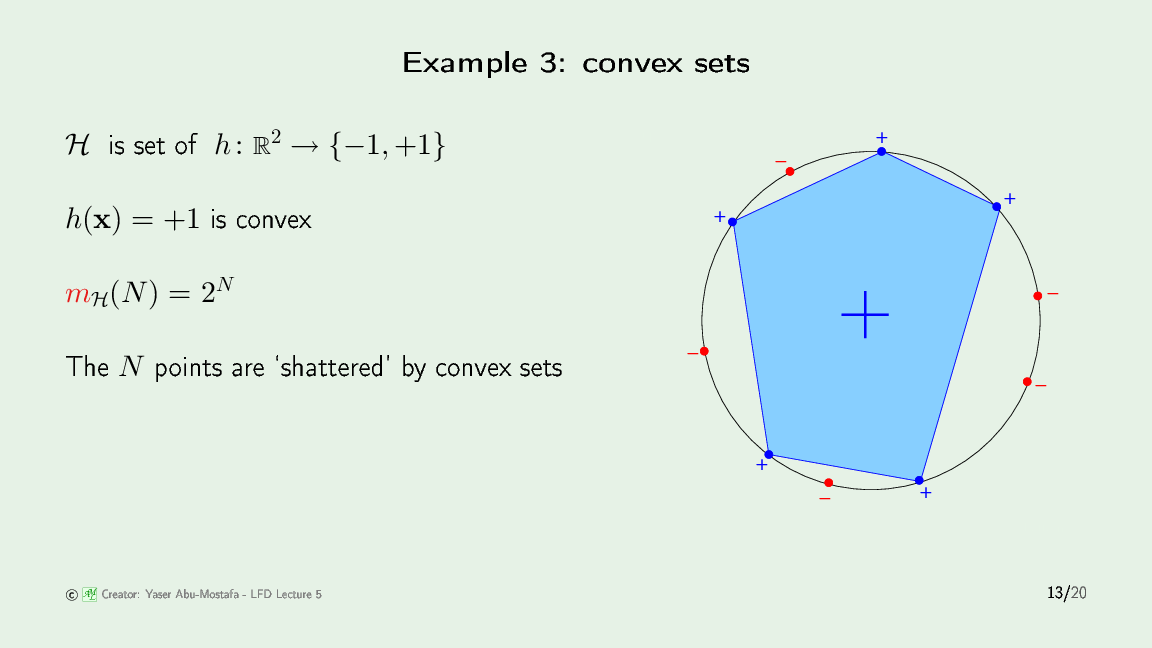
凸集可以把任意颜色配置的N个点完全分开,凸集里面是+1,外面是-1。所以它的growth function 是 $2^N$,凸集模型没有break point。
-
Break point k
-
无法用假设集 $\mathcal H$ 完全把两类点分开的点的个数 k。也就是开始出现 $m_{\mathcal H}(k) < 2^k$ 这种情况时的点数。
例如没有任何一种 4 个点的配置,能用2D perceptron 将其完全分开,所以 2D perceptron 的 break point 是 4:$m_{\text{2D percep}}(4) = 14 < 2^4$。大于4个的点集也不能被完全分开。
-
如果没有 break point, growth function is $2^N$.
如果存在 break point, growth function is a polynomial function in N : $\sum_{i=0}^{k-1} C_N^i$, whose maximum power is $N^{k-1}$.

