Table of contents
Convolution
-
对像素重新计数,并计算新的“像素值”的过程
-
卷积核从左上角开始,每次向左或向下滑动,并与其重叠的部分做内积(对应项相乘再求和)
-
提取特征
-
不做填充(valid padding),卷积后的输出尺寸为 $\lfloor\frac{n-k}{s}\rfloor+1$
-
图像尺寸:n×n
-
卷积核尺寸:k×k
-
步长:s
-
卷积核从左上角开始,每次向左滑动一列,最后停靠在右边缘,这时卷积核左侧的像素数再加上1(当前次),就是输出的尺寸 n-k+1。
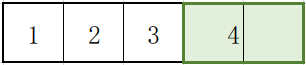
比如下图一行有5个像素,k=2,卷积核前面有3个再加上最后1个: 3+1 =4。
-
如果步长s=2,不能正好滑到最后,可以丢掉多余的部分或者填充像素。2
-
如果步长s=3,计算式应为:$\frac{n-k}{s}+1 = \frac{5-2}{3}+1 =2$
-
如果步长s=4,计算式应为:$\lfloor\frac{n-k}{s}\rfloor+1 = \lfloor\frac{5-2}{4}\rfloor+1 =1$
-
-
对于 same padding, 输出尺寸:$\lfloor \frac{(n+2\times p-k)}{s} \rfloor+1$
就是先对原始图像补充 p 圈像素,再做卷积。
Padding
- 在图像外围填充一圈或几圈像素,像素值通常为0
- 保证输出与输入的尺寸一致。1
- 常见两种padding:
- valid padding: 不填充,只使用原始图像
- same padding: 填充边缘,使卷积结果与输入尺寸一致。
为了使输出尺寸仍等于n,即:$\frac{n-k+2*p}{s}+1 = n$,解得:$p=\frac{(n-1)*s+k-n}{2}$;如果s=1,则 $p=\frac{k-1}{2}$。
Stride
- 卷积核滑动的步长 s
- stride=1,则卷积核每次向左滑动一列或者向下滑动一行
- 压缩信息:成比例缩小输出的尺寸,stride=2,则输出为输入的1/2。1
Pooling
- 保留特征,并减少计算量
-
max-pooling: 近视眼,只能看到最大的;
-
average-pooling
(2023-12-12)
F.avg_pool3d
Number of channels doesn’t change, and D, H, W shrink. Docs
|
|
MVSNet uses AvgPool3d to compute the sum of every 4 depth-probability planes:
|
|
Deconvolution
Complexity of CNN
ConvTranspose2d()
|
|
Deconvolution visualization
(2023-07-19)
torchvision.models.resnet34
ResNet - PyTorch | Source code
layers: [3,4,6,3] means that layer1 has 3 BasicBlock (resnet50 is Bottleneck) convolution blocks,
and layer2 has 4 blocks, and layer3 has 6 blocks, and layer4 has 3 blocks.
|
|
(2023-09-12)
F.pad
Padding an image along width, or height, or depth directions. Docs
-
The order of dimensions should be arranged according to Width, Height, Depth, e.g., padding the last 3 dimensions:
F.pad(x, (padding_left, padding_right, padding_top, padding_bottom, padding_front, padding_back) )So the order of (l,r,t,b,f,b) is reverse against an image tensor: (Depth, H, W)
nn.Conv3d
Input: (B, Ch_in, D, H, W); Output: (B, Ch_out, D_out, H_out, W_out)
-
For example, a tensor with shape of (2, 3, 4, 224, 224) is 2 video clips with 3 frames and each frame is a 4-channel image with size 224x224.
After convolution with a kernel of size (2, 4, 4), it can be transformed to (B=2, Ch_out=128, D=2, H=56, W=56)
Iterate each channel for
Dframes to convolve with a unique 3D kernel. Once every channel has multiplied by a kernel, all the 4 weighted channels are summed directly to form one of output channels.
Depthwise Convolution
(2023-07-25)
Separate a convolution into two steps:
-
Shrink the size of the feature maps using 1-channel plane-wise kernel (Depthwise Conv);
-
Expand the number of channels using 1x1 kernel (Pointwise Conv).
-
FLOPs reduced, but the IO access increased resulting in slower inference. Depth-wise Convolution - 沈景兵的文章 - 知乎
Expanding channels process costs the equal amount of FLOPs in normal convolution and pointwise convolution. For example, when expanding 3 channels to 256 channels, each pixel performs multiplication 256 times.
However, the depthwise convolution doesn’t multiply a kernel by each channel and sum them together, but only multiply a kernel by only one channel. A Basic Introduction to Separable Convolutions - Medium

-
Fewer parameters: 3x3x253 kernels are replaced with 1x1x256 kernels for every pixel on the resultant feature map.

(2024-06-22)
-
A video expalnation: Nik_Li - 15分钟看懂depthwise convolution
-
第一阶段的 depth-wise convlution 是一直不变的,#out channels 是由第二阶段的 point-wise convlution 做多次决定。
depth-wise 对比 传统卷积类比于:一个 Encoder(第一阶段固定) 和 多个 Decoder(多个输出通道); 而传统卷积层是:每个输出通道的“输入量”是不一样的(第一阶段不固定),每一次卷积就是一个 encoder-decoder 组合。
-
如果只有一个输出通道,两种卷积是等价的,因为表达式可以写成一样的。 如果是有多个输出通道,那么就需要求 Encoder 需要有很好的能力,支持被不同的 “decoder” 解释成不同的输出,以对应不同的信息
-
Reference
- (accessed Dec. 22, 2021).