Table of contents
Code-matlab | Code-python | paper
Intuitive from Shakil
Goal
Find the true matched keypoints and identify the outliers.
Affinity matrix
Measure the difference between any two edges in two graphs.
c is the outlier. Nodes can be SIFT feature points.
$$W_{1a,2b} = 12 - ab$$The index of each element is a notation representing if i was a and if j was b.
| W | 1a | 1b | 1c | 2a | 2b | 2c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 0 | |||||
| 1b | 0 | |||||
| 1c | 0 | |||||
| 2a | 0 | |||||
| 2b | 0 | |||||
| 2c | 0 |
Random walk
Iterations will not walk out of the area, i.e., the middle area has higher probability.
| a | b | c | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| probability | node |
|---|---|
| 0.75 | a |
| 0.1 | b |
| 0.05 | c |
| 0.25 | a |
| 0.5 | b |
| 0.25 | c |
The initial probility for each point is the same: 1/6:
| probability | node |
|---|---|
| 0.16 | a |
| 0.16 | b |
| 0.16 | c |
| 0.16 | a |
| 0.16 | b |
| 0.16 | c |
Associate graph
(2023-07-09)
Abstract
- Association graph consistitue of nodes representing correspondence between two graphs.
- Random walk select nodes to enforce real correspondence on the association graph.
Introduction
-
Previous work didn’t make a objective function
-
IQP is NP hard, so its solution needs approximation.
-
Random walk view: rank the nodes on the association graph.
-
Previous methods
- Tensor eigen decomposition
Problem
-
Each graph have a set of nodes (vertices) 𝐕, edges 𝐄, and attributes 𝐀.
- node is local appearance of feature
- edge is geometrical relationship of two nodes.
-
Matching two graphs is to find the correspondence of nodes in two graphs
-
Affinity matrix 𝐖 is recording the compatibility of pairs of edges
- diagonal is unary affinity, e.g. $𝐖_{ia;ia}$, between one correspondence and itself.
- non-diagonal $𝐖_{ia;jb}$ is the affinity of a pair of correspondence: $(vᵢᴾ,\ vₐ^Q)$ and $(vⱼᴾ,\ v_b^Q)$
W ia ib ic ja jb jc ia ib ic ja jb jc Each row is fixing one correspondence in one pair of correspondences, and changing the other correspondence.
For example, 1 corresponds to a is fixed, then the neighbor of 1 and a is changing:
-
The correspondence assignment is stored in assignment matrix 𝐗;
- where 1 means matched correspondence, while 0 means the two nodes are not matched.
x a b c i j -
Column vector 𝐱 is the reshape of matrix 𝐗 with length of $nᴾ×n^Q$
x_ia x_ib x_ic x_ja x_jb x_jc -
Indicator vector 𝐱* is the target by maximizing the score of 𝐱ᵀ𝐖𝐱
Random Walks for Graph Matching
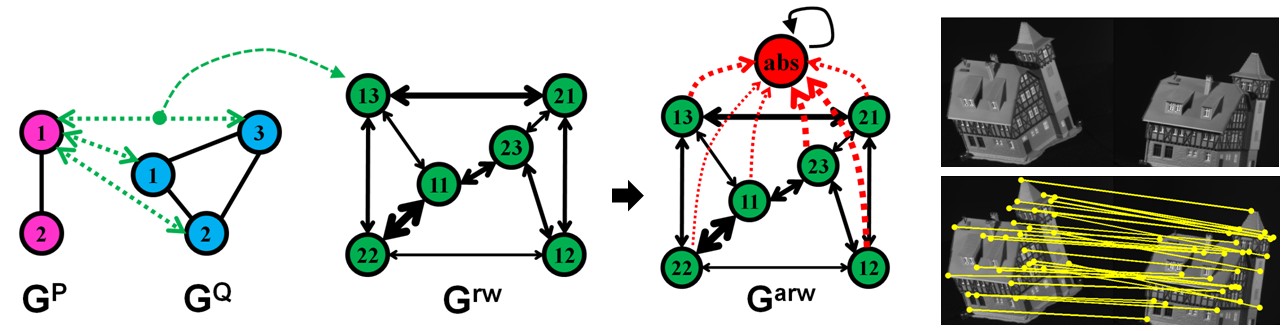
Convert the affinity matrix to an association graph for random walk
-
Association graph $G^{rw}$ is made up by nodes that represents a correspondence between $Gᴾ$ and $G^Q$.
For example, the correspondence $(vᵢᴾ,\ vₐ^Q)$ is node $v_{ia}$ on the association graph.
-
so the edge attributes are the elements of affinity matrix 𝐖 ;
For example, the edge $e_{ia; jb}$ on the association graph is the affinity $𝐖_{ia;jb}$
-
Ranking the nodes of association graph by random walk process
Affinity preserving random walk
-
Random walk process:
A walker starts off with an arbitrary node and select as the next step one of its out-going edges based on the Markov transition kernel.
-
Internet democracy:
Total vote that every webpage has is 1. This is realized by dividing the weight of its every out-going edge by the total number of its out-going edges.
-
Row stochastic:
On to the association graph, its edges set 𝐖 is supposed to be normalized by 𝐃. That is each row is divided by the sum of the affinity values in that row. Then the normalized affinity matrix is row stochastic matrix 𝐏 = 𝐃⁻¹, where 𝐃 is a diagonal matrix.
-
However, because there are outliers on the association graph, which are suppose to have small weight, the Internet democracy doesn’t suit here. -
Outliers on the association graph are the mismatched correspondence.
For example, the actual corespondences are $(v_1^P, v_1^Q)$, and $(v_2^P, v_2^Q)$, which are nodes $v_{11}$ and $v_{22}$ on the association graph.
Therefore, on the association graph, the outliers are nodes other than $v_{11}$ and $v_{22}$, i.e., $v_{12},\ v_{13},\ v_{23},\ v_{21}$