Table of contents
ResNet
Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition ~ 2015 MSRA CVPR arxiv
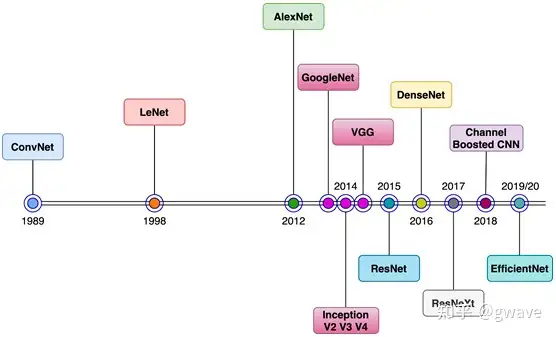
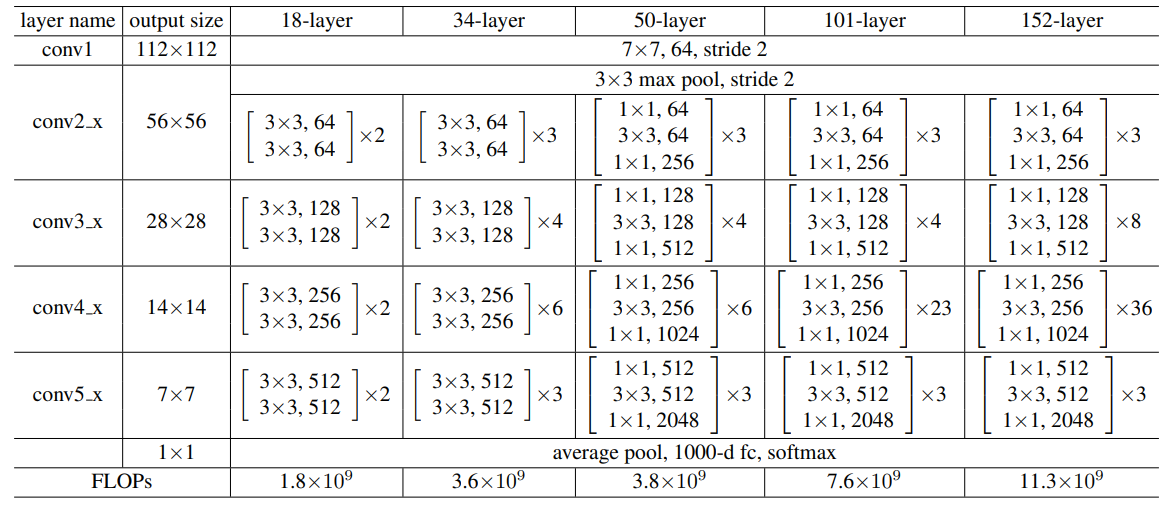
Network Architectures:
Bottleneck Block:
Figure 5: A deeper residual function ℱ for ImageNet. Left: a building block (on 56×56 feature maps) as in Fig. 3 for ResNet-34. Right: a “bottleneck” building block for ResNet-50/101/152.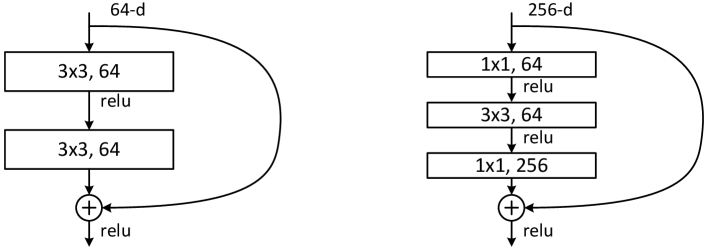
Code: torchvision
MobileNet
MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications ~ 2017 Google arxiv
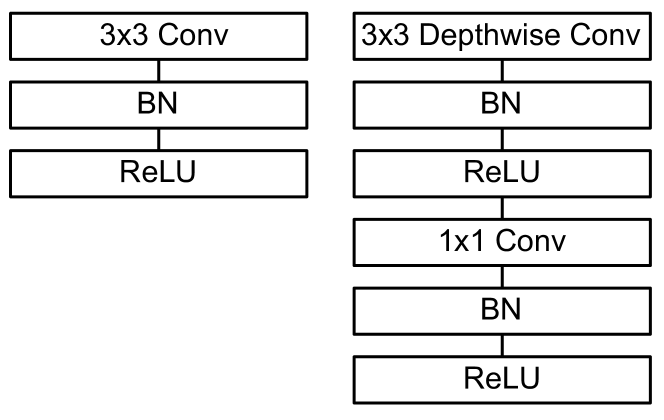
Figure 3: Left: Standard convolutional layer with batchnorm and ReLU. Right: Depthwise Separable convolutions with Depthwise and Pointwise layers followed by batchnorm and ReLU.
- Depthwise + Pointwise convolution reduces FLOPs and parameters.
- Accuracy is slightly inferior to fully CNN
MobileNet V3
Searching for MobileNetV3 ~ 2019 Google ICCV arxiv
Architecture of MobileNetV3-Large:

Table 1 Specification For Mobilenetv3-Large. SE Denotes Whether there Is A Squeeze-and-Excite In That Block. NL Denotes the Type of Nonlinearity Used. Here, HS Denotes H-Swish and RE Denotes Relu. NBN Denotes No Batch Normalization. S Denotes Stride.
Code: torchvision
EfficientNet
EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks ~ 2019 Google ICML arxiv
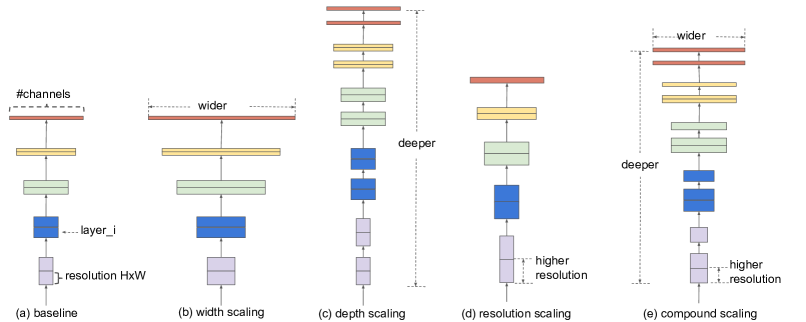
Figure 2:Model Scaling. (a) is a baseline network example; (b)-(d) are conventional scaling that only increases one dimension of network width, depth, or resolution. (e) is our proposed compound scaling method that uniformly scales all three dimensions with a fixed ratio.
Summary:²
- Scale proportionally the resolution and channels of feature maps, and number of blocks in a model.
- Use NAS (Neural Architecture Search) to search a structure for smaller models.
Architecture:
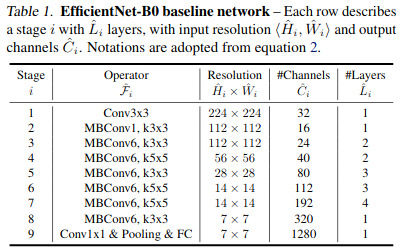
MBConv block is similar to MobileNetV3 InvertedResidualBlock. 8
Code: torchvision
Vision Transformer
An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale ~ 2020 Google ICLR arxiv
-
Convert an image (224x224) to a vector using a 16x16 kernel with a stride of 16 and then flattening the result feature map (14x14) into a sequence (196).
-
By performing 728 times convolution for getting 728 vectors, an image is represented by a matrix (196, 728).
-
To encode this image’s information into a vector for classification, the class label are concatenated onto each vector and Positional encoding is added element-wise onto each vector.
-
Then this matrix (197, 728) gets passed through Multi-head Self-Attention so that each token (728) will obtain a vector recording the similarity (mutual information?) between it and each other token.
-
Only taking out the vector belonging to the class label, it will be projected to the number of target categories for classifing.
The hybrid model didn’t downsample the image by a 16x16 kernel, but use ResNet50 to shrink the 224x224 image to 14x14.
- When training fewer epochs (7), hybrid model has higher accuracy than standard ViT. However, more epochs will make ViT better than hybrid model.
ViT needs pre-traine on a large dataset (Google JFT) to perform better on ImageNet. However, if it’s trained on ImageNet-1K directly, the result won’t be good.
Swin Transformer
Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows ~ 2021 MSRA ICCV arxiv
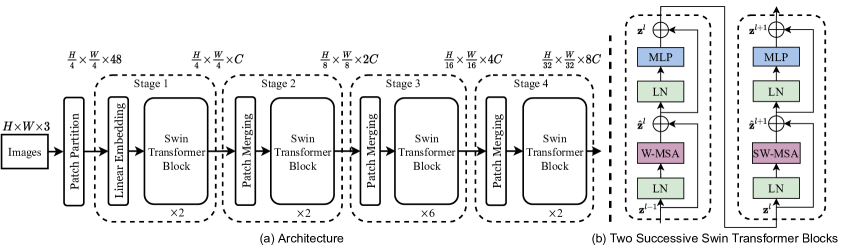
A unit component of swin transformer has two blocks: a Window MSA and a Shifted Window MSA.
-
Patch merging
Image from 5 -
Window MSA
-
Instead of performing MSA for the all patches (sequence) of a feature map, a feature map is divided into finer grid, where severl patches is a group and a group of patches perform MSA.
-
This way reduces computation.
-
Disadvantage is that the context between different group isn’t built.
-
-
Shifted Window MSA
-
Move the grid (H/2, W/2) patches to the bottom right, then different groups can be fused through MSA.
-
To enhence parallelization, top row of patches are moved to the bottom and the left-most column of patches are moved the right-most.
-
To avoid fuse non-neighbor patches that are not adjacent in the original feature maps, masked MSA is used.
The masks are added onto the q-k weights corresponding to the non-neighbor patches for the current patch (q).
-
(2023-09-28)
Split windows
1 image, 2 channels, H=4, W=6
|
|
|
|
The above 3 steps are equivalent to: e = rearrange(a, "B C (nh H) (nw W) -> (B nh nw) H W, nh=2, nw=2)
Restore feat maps
.permute() changed .stride(), which can’t return to the structure that matches with the tensor’s original shape anymore.
Therefore, .contiguous() is necessary before tensor .view() to the original size.
|
|
Code from MatchNeRF.
ConvNeXt
A ConvNet for the 2020s ~ 2022 FAIR CVPR arxiv
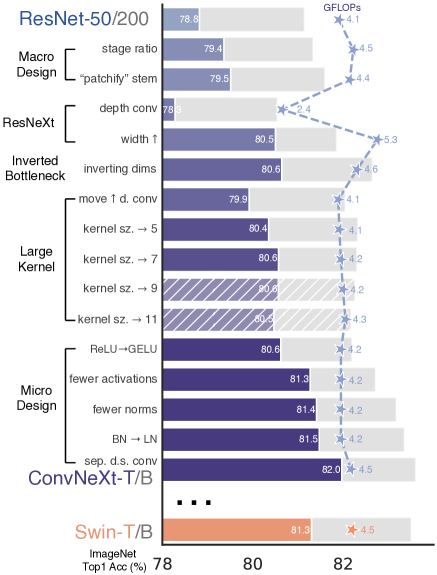
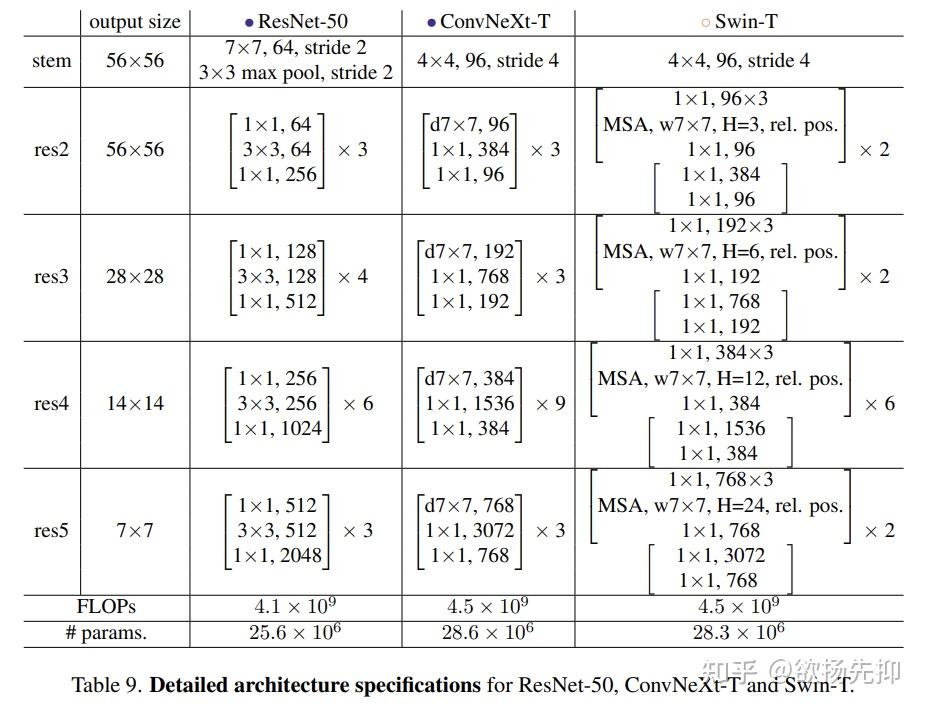
Modify ResNet50 according to Swin Transformer: 4
- Stages: [3, 4, 6, 3] ➡ [3, 3, 9, 3] (Tiny) ³
- Stem: First
conv1(kernel=7x7, stride=2, pad=3) andmaxpool(stride=2) ➡Conv2dNormActivation(kernel=4x4, stride=4) - Depthwise Conv: groups=1 ➡ groups=input_channels
- Expand Input Chanls: Stage 0
4=(64,256,512,1024,2048) ➡ Stage 04=(96,192,384,768) - Expand Middle Chanls: Bottleneck (256➞64➞64➞256) ➡ Inverted Bottleneck (96➞384➞384➞96)
- Conv First: fc + conv + fc ➡ conv + fc + fc.
Because in a transformer block, attention is ahead of fc.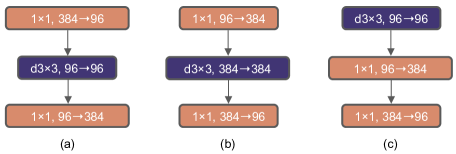
- Large Kernel: 3 ➡ 7
- Activation: ReLU ➡ GELU
- Fewer Activation: After each Conv2d ➡ After 1st 1x1 conv
- Fewer Norms: After each Conv2d ➡ After 1st 7x7 conv
- Norms: BatchNorm ➡ LayerNorm
- Downsample Layer: Conv(stride=2) ➡ LayerNorm + Conv2d(k=2,s=2)
A ConvNext block mimics a transformer block: attention + feedforward (MLP), so Multi-Head Self-Attention corresponds to Depthwise Conv, and feedforward corresponds to 1x1 conv + activation. 6
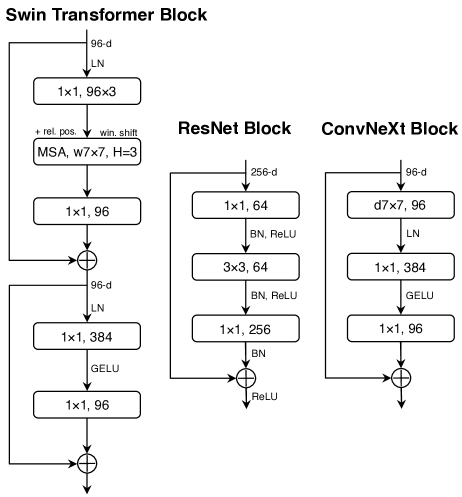
Network Architecture:
Code flowchart from 4
Codes: torchvision | csdn-AI浩 | official
Reference
-
(Found this under the Images section of DDG with searching “convnext model”)