Table of contents
一句中文:构建 point-alinged feature field, 然后用 attention 把特征融合成图像,特征的attn score 反映了深度
Insights:
-
NeRF is in a backward optimization fashion. The color is mapped to points along with the optimization. So the radience field is recovered backward. While Generalizable NeRFs assign feature onto points in the feed-forward process.
-
Projecting the points onto feature maps exerts the inductive bias of epipolar constraints for injecting geometry prior.
-
It’s inferior to NLF
-
Samples on a single ray cannot recover refraction and scattering, in which the ray will bend. So GNT managed this by its view transformer?
-
Occlusion-aware is realized by giveing the most visible reference view the most weight. Depth-aware is endowed by the importance of each point to the pixel color. “importance=density”
-
GNT doesn’t care the quality of 3D geometry reconstruction.
Only net_coarse is used and trained with 4096 rays, 192 N_samples in one iteration. They didn’t split the N_rand into chunks in the train.py, but they did when rendering a full imagein evaluation period. So I need to distribute the 4 blocks onto 4 crads for accomodating the 4096 rays in one batch, if I want to reproduce their expriment. In my previous training, the number of points fed into MLP is N_rand x N_samples = 2048x64 = 131072.
Abstract
- Generalizable NeRF Transformer (GNT)
- two transformer-based stages
- view transformer: multi-view geometry, coordinate-aligned features, epipolar lines
- ray transformer: ray marching rendering, decode point features
- reconstruct single scene without rendering formula
- attention map
1 Introduction
-
Topoic: novel view synthesis by NeRF (coordinate-based model + differentiable volumetric rendering)
-
Problems: one network overfits one scene with long optimization.
-
Former solutions & drawbacks: Ibrnet, pixelNerf, NLF proved the coordinates are not necessary, but the novel view can be interpolated from other views’ image features.
-
Task:
-
Contributions & Reason
- cooridnate network and volumetric renderer are composed into a transformer architecture.
- use multi-view image features to infer coordinate-aligned features. Later these features are decoded to novel view directly without volume rendering.
-
Results statement
有泛化能力意思是,训练好的模型可以直接用输入图像重建 unseen 场景的新视图?
2 Related Work
-
Advances in Transformer
-
Neural Radiance Fiels: NeRF, Mip-NeRF; surface representation, dynamic scenes, reflection modeling; Generalization nerf: PixelNeRF, IBRNet, MVSNeRF, NeuRay; accelerate nerf.
-
Transformer Meets Radiance Fields: IBRNet, NerFormer, Generalizable neural radiance field, NLF, Vision transformer for nerf-based view synthesis; SRT
3 Preliminaries
4 Method: Make Attention All NeRF needs
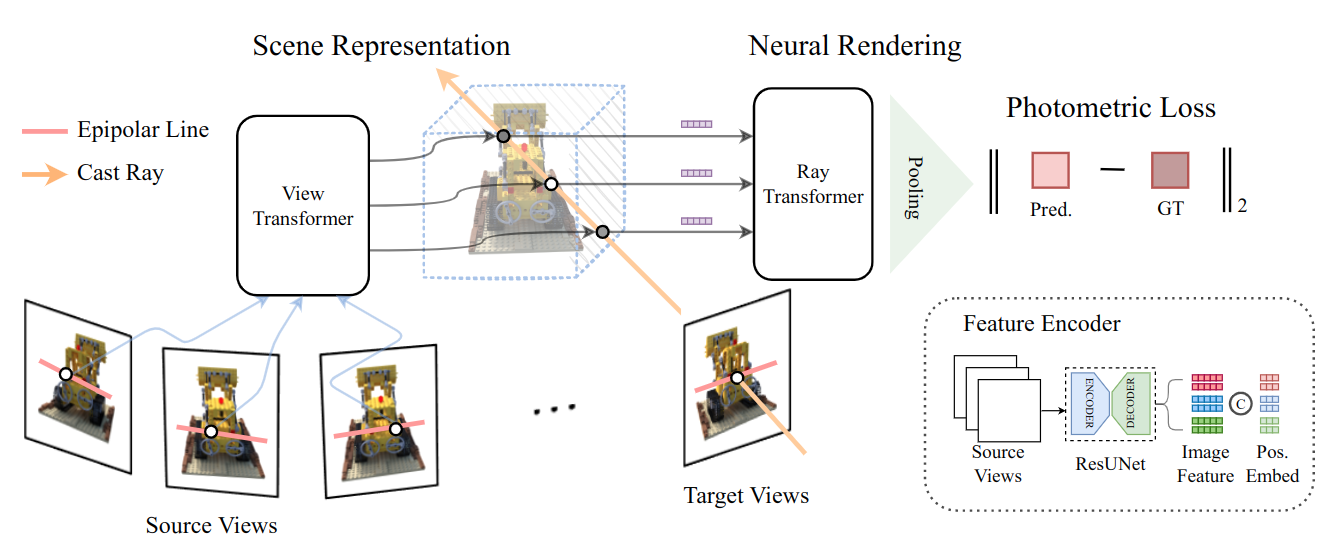
4.1 Epipolar Geometry Constrained Scene Representation
-
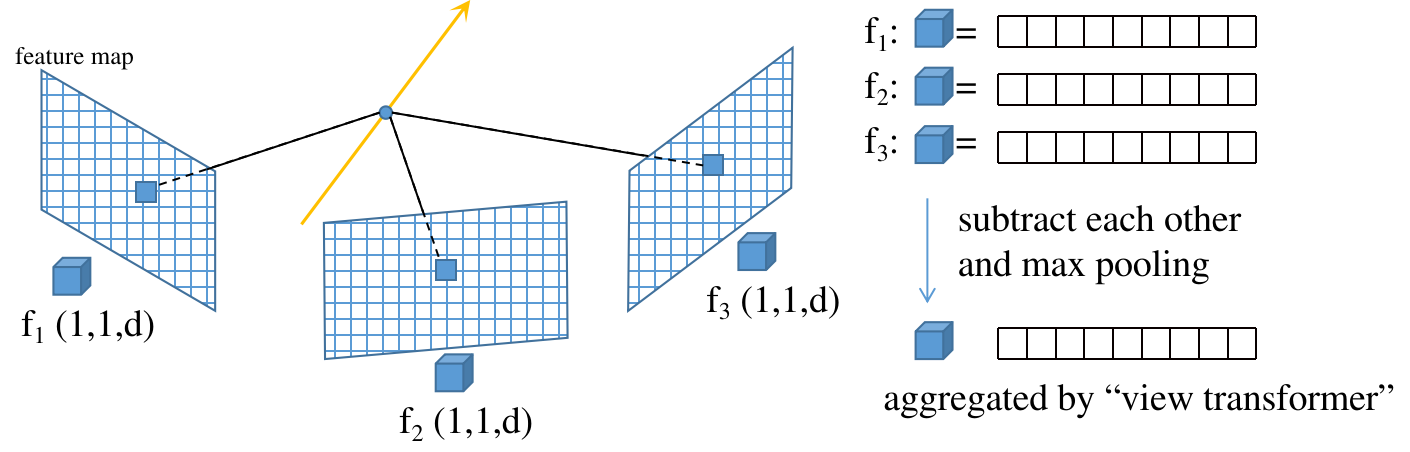
Multi-View Feature Aggregation.
-
Vanilla NeRF use MLP to parameterize scene in a backward optimization fashion? (先渲染出图片,依据图片误差再返回去更新辐射场)
-
In contrast, generalizable NeRFs construct the radiance field in a feed-forward scheme
用图像特征优化辐射场,训练好后,就可以对辐射场应用volume rendering来渲染新视图;而本文是从辐射场映射回图像特征,从而生成新视图(2023-12-16) NeRF 是从待渲染的像素出发,向空间发出射线,去查询颜色。而 Forward 是把空间点投影到像素上。
-
Represent the scene as a feature field, where each point in the space has a part of image feature.
-
Use attention to fuse all pixel on ResUNet feature maps of source views is memory prohibitive
Only fuse the pixels locating in the paring epipolar lines of “neighboring views” (和 PixelNeRF 一样,不过人家没提对极几何这个词,就是把光线上的点投影到不同视图上)
-
-
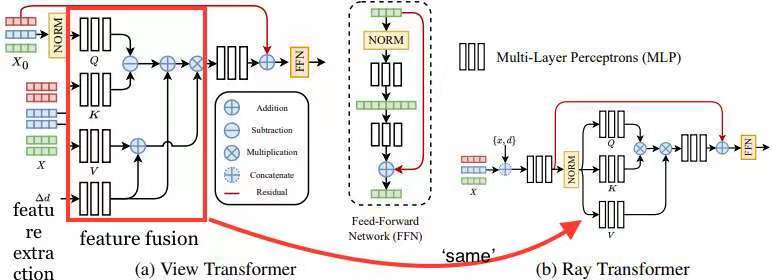
Memory-Efficient Cross-View Attention
-
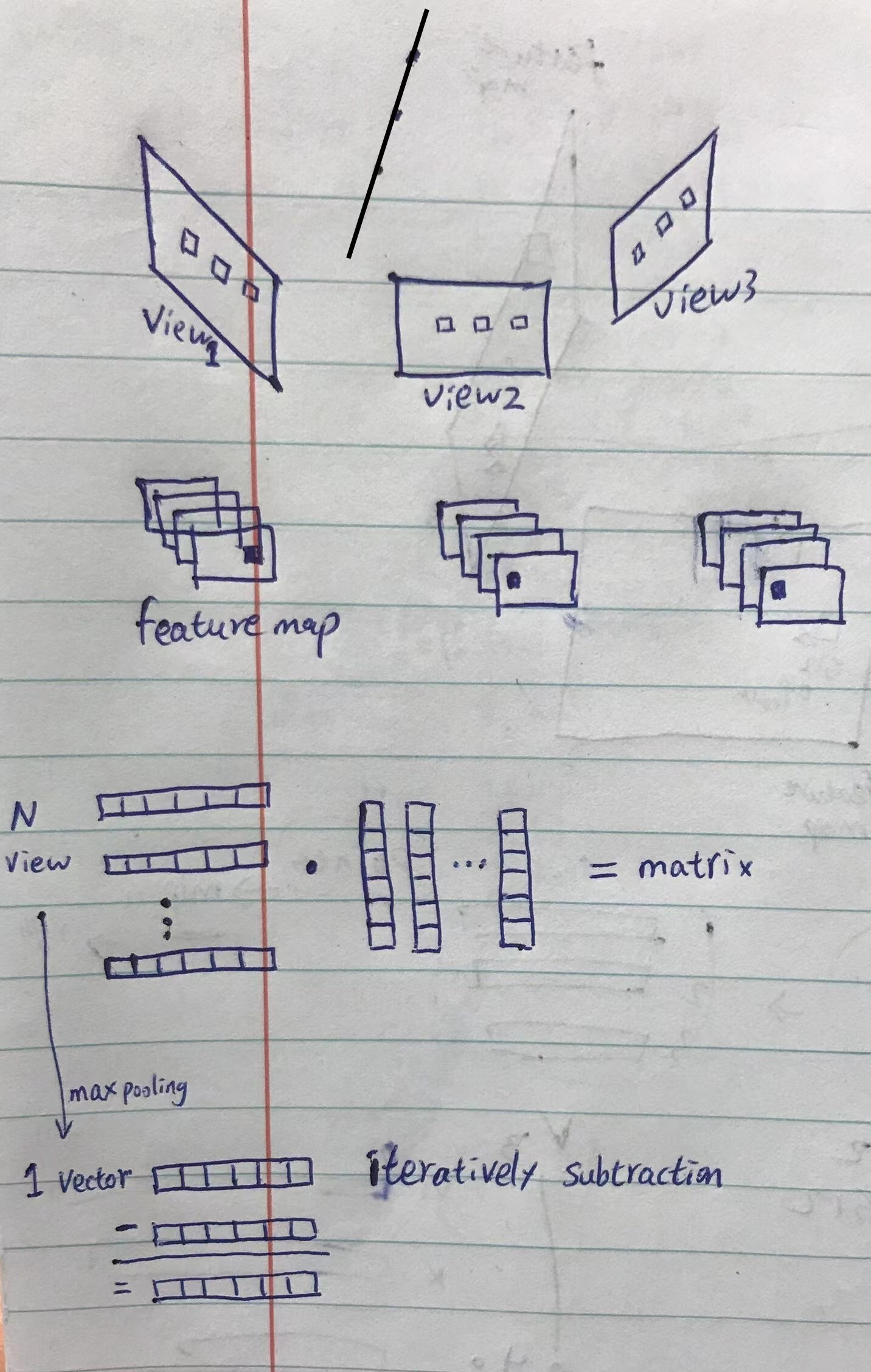
Only use one read-out token in the query sequence to iteratively fuse features from neighbor views
-
The similarity is not computed by dot multiplication, but subtraction, so the attention score is calculated for every channel of the features.
-
The attention scores matrix and ‘V’ are added by the relative directions between source views and the target view.
-
-
Discussion on Occlusion Awareness.
4.2 Attention Driven Volumetric Rendering
Different illumination effects and material scenarios need to apply specific handcrafted rendering formula. Data-driven renderer decode the image features into images realizing various phenomena in one way.
-
Ray Feature Aggregation:
- Analogy the token features as the color in the volum rendering fomula. Therefore, do attention for coordinate-aligned features to aggregate the final color (rgb) for the novel pixel/ray.
- mean pooling to compress the feature patch into a pixel
- use dot-product attention to fully mix features of other points getting comprehensive contextual information.
- 关于 auto-regressive rendering 的延伸讨论?
-
Discussion on Depth Cuing
- depth is the average of marching distance with attention score
- NLF 有相同的架构,区别在哪?
5 Experiments
single scene; generalization to unseen scenes
5.1 Implementation Details
- Source and Target view sampling
在 Blender 数据集上的 PSNR 无明显提升
(2023-08-16)
Code
train.py
\begin{algorithm}
\begin{algorithmic}
\PROCEDURE{train}{args}
\STATE data: [
rgb$_{(1,H,W,3)}$, $\newline\qquad$
camera$_{(1,34)}$, $\newline\qquad$
rgb\_path$_{(str)}$,$\newline\qquad$
src\_rgbs$_{(8,H,W,3)}$, $\newline\qquad$
src\_camera$_{(8,34)}$, $\newline\qquad$
depth\_range$_{(1,2)}$
]
\STATE $\newline$
\STATE ray\_sampler = RaySamplerSingleImage(data)
\STATE ray\_batch = ray\_sampler.random\_sample(N\_rand)
\STATE featmaps = model.feature\_net(ray\_batch["src\_rgbs"])
\STATE ret = render\_rays(ray\_batch, model, projector, featmaps)
\ENDPROCEDURE
\end{algorithmic}
\end{algorithm}
llff_test.py __init__() of a training dataset:
|
|