Table of contents
一句话:用图像特征训练NeRF,(所以有泛化能力,不局限于单场景,不像nerf只做优化)
![]()
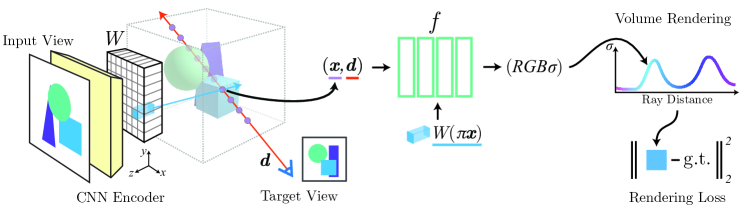
如图1,光线是随机从像素空间选择的(为了随机选一些(N个)空间点),空间点投影到不同视图的 feature maps (512 chnls) 上,得到 (N∗Nviews个) feature volume,送入 mlp 变换成 r,g,b,density,再做 volume rendering
Abstract
- NeRF conditioned by few images
- costly independent optimizing
- use convolution to learn scene prior
- no explicit 3D supervision
- single image novel view synthesis task
1 Introduction
-
Topic: Synthesis novel views for a scene from sparse views
-
Problem
-
Former solution & drawbacks:
- Differentiable neural rendering: represent the sence as a neural network which generates rendered images
- NeRF: encode the 3D position and view dirs to volume density and color. It needs too many images.
-
Task: predicting NeRFs from one or several images.
-
Contributions: Utilize pixel-aligned spatial image features to learn scene priors (specifically) Input image → convolutional feature grid → 𝐱,𝐝,feature(residual) → NeRF (pool-based multi-view features fusion) → σ,rgb
-
Results statement
- no 3D supervision: 3D shape or object masks
- not trained in a canonical coordinate system, but in each camera coordinate system
- “convolution preserves the spatial alignment between the image and the output 3D representation”
- flexibility on number of input views in test period
(Experiments) ShapeNet; DTU
2 Related Work
- Novel View Synthesis
- Learning-based 3D reconstruction
- Viewer-centric 3D reconstruction
3 Background NeRF
- (job) (input-output) x,d -> density, color
- (training manner) volume rendering
- (loss func)
- Limitation: only use geometric consistency, resulting in individual optimization for every view
4 Image-conditioned NeRF
-
(improvement) input spatial image features into network. (Specifically) Two components: convolutional encoder + nerf mlp. Spatial query position is drawn from camera space.
-
(paragraph order) From simple case to general case
4.1 Single-Image pixelNeRF
- (main idea) The inputs are all from view space.
- (steps) Input image → feature volume W=E(I) → assign image feature to sample points by projecting the 3D position to 2D location → NeRF network
- (pipeline)
- (the role of query view direction)
4.2 Incorporating Multiple Views
-
(main idea) extract information from multi views to resolve geometric ambiguities and able to accept multiple images in test time. No relation with world space
-
World space can base on any view. (notion explain)
-
Project the world query point into each input view space. The fisrt layer processes each view independently and the final layer aggregates all views.
-
(model pipeline)
- Encode each input img into feature volume and retrieve the corresponding feature at the sample point’s projecting location.
- The features companied with (xyz,viewdirs) are input to the first layer and all the intermediate vectors are fused by average pooling before entering the final layers, which compress the vector into density and color.
5 Experiments
-
Datasets:
- ShapeNet (category-specific and category-agnostic view synthesis);
- ShapNet scenes with unseen categories and multiple objects;
- DTU rescaled to 1/4: 400x300
-
Baselines: SRN, DVR
-
Metrics: PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS
-
Implementation Details:
- Image encoder: ResNet34;
- Features: non-pooling, upsampled using bilinear interpolation, concatenated feature maps of every image.
- Combine the points’ position and view direction in a ResNet manner (residual)
5.1 ShapeNet Benchmarks
ShapeNet for category-specific and category-agnostic
Category-specific View Synthesis Benchmark
-
one-shot and two-shot view synthesis
-
A model is trained for reconstructing one category and the used images contains 50 random views per object instance. Only 2 are encoded and fed into network.
-
Ablations. The benefit of local features
Category-agnostic Object Prior
- Train a single model to the 13 largest categories of ShapeNet
- pick one view randomly from 24 fixed elevation view of each object instance.
5.2 Pushing the Boundaries of ShapeNet
-
(tasks) less controlled capture scenarios in ShapeNet:
- unseen object categories,
- multiple-object scene,
- simulation-to-real transfer on car images.
-
Generalization to novel categories: apply the model on unseen categories
-
Multiple-object scenes: The geometric features need can be applied in any view direction (360°)
5.3 Scene Prior on Real Images
Code
(2023-07-20)
calc_losses():
\begin{algorithm}
\caption{Main steps of clac$\_$losses()}
\begin{algorithmic}
\PROCEDURE{clac-losses}{}
\STATE Sample 4 objects from 88 training scanned objects (folder) as a super batch
\STATE Each object samples randomly 1 or 3 from its total of 49 NV as target images for training
\STATE Sample a batch of rays (N$\_$rand)
\STATE Extract latent feature maps `self.latent`
\STATE Sample z$\_$coarse points on the rays
\STATE Transform points onto NS camera space
\STATE Perspective project xyz to 2D location uv on feature maps
\STATE Indexing latent vectors from feature maps by `F.grid$\_$sample()`
\ENDPROCEDURE
\end{algorithmic}
\end{algorithm}
(2024-06-06)
-
NeuRay: PixelNeRF is an analogy to stereo matching. Intro
MVSNet projects multiple hypotheses depth planes onto source images (feature maps) and then matches multi-view features with a UNet. Similarly, PixelNeRF projects multiple points on each ray at sampled depth onto the source images.
-
MVSNet don’t have the problem of occulsion because all it deals with is a photo (plane) without 3D structure from begining to end.
Whereas NeRF handles the entire 3D space, the occulusion could happen when viewpoint changes.
NeuRay use image features to determine if a sample point on a ray is visble or not.
DTU dataset
(2023-08-17)
get_split_dataset() (in “data/init.py”) will construct different Dataset objects for different datasets.
|
|