Table of contents
Code | Arxiv(2308) | ProjPage
Code: wanmeihuali/taichi_3d_gaussian_splatting
Video Explain
(2023-09-11)
Source video: 【论文讲解】用点云结合3D高斯构建辐射场,成为快速训练、实时渲染的新SOTA!- 意の茗
-
CG technique: Splatting
-
Each point is an anisotropic 3D Gaussian distribution:
- mean is point location (xyz),
- covariance matrix determined the shape of the 3D Gaussian
-
Optimize points’ distribution:
- Locations are at mean, which are needless to learn;
- Co-variance matrix is converted to quaternion
-
3D Gaussian distribution can do clone and split to fit complex geometry.
-
Tile-based fast rendering rather volume rendering.
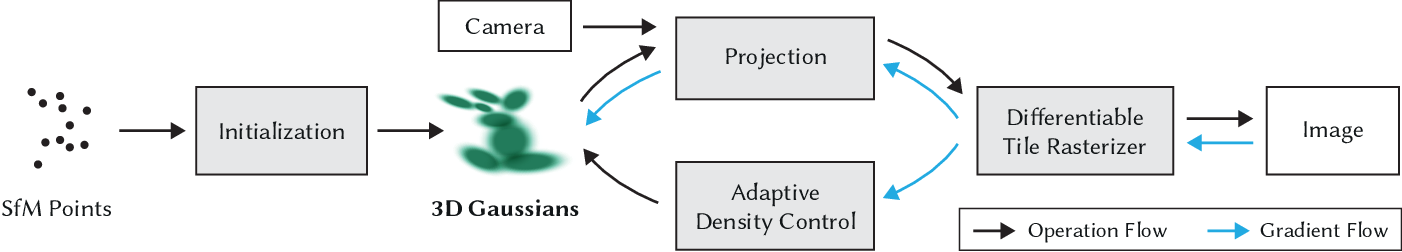
3D Gaussian
(2023-10-28)
-
1D Gaussian distribution:
Given a scalar $x \sim N(μ,σ²)$, its PDF:
$$ p(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2πσ²}} e^{-\frac{(x-μ)²}{2σ²}} $$ -
3D Gaussian composed of 3 independent 1D Gaussian in 3 directions can be represented as below.
Given a vector 𝐯: [a,b,c], its PDF: p(𝐯) = p(a) p(b) p(c)
$$ \begin{aligned} p(𝐯) &= \frac{1}{(2π)^{3/2}σₐ σ_b σ_c} exp(-\frac{(a-μₐ)²}{2σₐ²} -\frac{(b-μ_b)²}{2σ_b²} -\frac{(c-μ_c)²}{2σ_c²}) \\\ (\text{vectorize}) &= \frac{1}{(2π)^{3/2} |Σ|^½} exp(-½⋅(𝐯-\bm μ)ᵀ(𝐯-\bm μ) Σ⁻¹) \end{aligned} $$-
Where the $σₐ σ_b σ_c$ is the square root of the determinant of covariance matrix Σ:
$$ |Σ|^{½} = \begin{vmatrix} σₐ² & 0 & 0 \\\ 0 & σ_b² & 0 \\\ 0 & 0 & σ_c² \end{vmatrix}^{1/2} = σₐ σ_b σ_c $$ -
The exponent can be derived as:
$$ \begin{array}{ccc} \begin{bmatrix} a-μ_a \\\ b-μ_b \\\ c-μ_c \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} a-μ_a & b-μ_b & c-μ_c \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} 1/σₐ² & 0 & 0 \\\ 0 & 1/σ_b² & 0 \\\ 0 & 0 & 1/σ_c² \end{bmatrix} \\\ = \frac{(a-μ_a)²}{σₐ²} + \frac{(b-μ_b)²}{σ_b²} + \frac{(c-μ_c)²}{σ_c²} \end{array} $$ -
If those 3 1D Gaussian are all $N(μ=0, σ²=1)$, the 3D Gaussian becomes simpler:
$$\rm p(𝐯) = \frac{1}{(2π)^{3/2}} exp(-\frac{a²+b²+c²}{2})$$
-
-
Derivation for arbitrary 3D Gaussians:
-
3D Gaussian is a product of three 1D Gaussian. If each 1D Gaussian is N(0,1), then 3D Gaussian is:
$$ \begin{aligned} p(𝐱) &= p(x)p(y)p(z) \\\ &= \frac{1}{(2π)^{3/2}} exp(-\frac{x²+y²+z²}{2}) = \frac{1}{(2π)^{3/2}} exp(-\frac{𝐱ᵀ𝐱}{2}) \\\ \end{aligned} $$ -
For an arbitrary vector 𝐱 = [x,y,z], where 3 Gaussians could be in various shapes. it will be moved to the origin of world space by subtracting the mean vecotr, and the 3 directions (covariance matrix) will be scaled to 1 (identity matrix) through a transformation matrix 𝐀.
$$\rm 𝐱' = 𝐀(𝐱-\bm μ)$$Because the mean vector is point’s position. This step means all points are moved to world’s origin and reshaped into a unit space for later optimization.
-
Plug this “normalized” 𝐱’ into 3D Gaussian :
$$p(𝐱') = \frac{1}{(2π)^{3/2}} exp(-\frac{(𝐱-\bm μ)ᵀ𝐀ᵀ𝐀(𝐱-\bm μ)}{2})$$ -
To reach a form about 𝐱, integrate p(𝐱’):
$$1 = ∭_{-∞}^{+∞} \frac{1}{(2π)^{3/2}} exp(-\frac{(𝐱-\bm μ)ᵀ𝐀ᵀ𝐀(𝐱-\bm μ)}{2}) d𝐱'$$ -
Substitude $d𝐱'$ with $d𝐀(𝐱-\bm μ) = |𝐀|d𝐱$
$$1 = ∭_{-∞}^{+∞} \frac{|𝐀|}{(2π)^{3/2}} exp(-\frac{(𝐱-\bm μ)ᵀ𝐀ᵀ𝐀(𝐱-\bm μ)}{2}) d𝐱$$The function being integrated is p(𝐱). Since 𝐱 follows Gaussian, it can be rewritten with a mean vector 𝛍 and a covariance matrix 𝚺.
-
The covariance matrix 𝚺 is a symmetric matrix, which can be decomposed by SVD:
$$ \begin{aligned} Σ &= U Λ Uᵀ \\\ &= UΛ^{½} Λ^{½T} Uᵀ \\\ &= UΛ^{½} (UΛ^{½})ᵀ \end{aligned} $$-
On a 2D plane, SVD is strecting and rotating, represented separately by a stretch matrix (diagnoal) $S = [^{s₁ \ 0}\_{0\ s₂}]$, and a rotate matrix (UUᵀ=1) $R = [^{cosθ \ -sinθ}\_{sinθ \ cosθ}]$.
-
Each column of U is orthogonal to each other and of magnitude 1. For example, when U is R:
-
In 3D space, matrices are 3×3.
-
𝐔 is a basis (a component, a coordinate system). By multiplying it with a diagnoal matrix, $UΛ^½$ is a linear transformation, denoted as the transformation matrix 𝐀. Thus, 𝚺 = 𝐀𝐀ᵀ.
In other words, an identity matrix (basis) will be transformed to another basis $UΛ^½$ by 𝐀.
Therefore, 𝐀ᵀ𝐀 = 𝚺⁻¹, which will reverse an arbitrary covariance matrix 𝚺 to identity matrix 𝐈, i.e., putting the ellipsoid into the “unit” space $[^{100}_{^{010}\_{001}}]$, where the modulus of each axis is 1.
-
-
Substitute 𝐀ᵀ𝐀 with 𝚺⁻¹, and $|𝐀| = |Σ|^½$, the 3D Gaussian is the function being integrated:
$$\frac{1}{(2π)^{3/2}|Σ|^½} exp(-\frac{(𝐱-\bm μ)ᵀΣ⁻¹(𝐱-\bm μ)}{2})$$ -
The 3D Gaussian used in this work is simplified as:
$$ G(x) = exp(-\frac{(𝐱)ᵀΣ⁻¹(𝐱)}{2}) \tag{4} $$-
Omit the mean vector 𝛍, becuase it’s 0. Every 3D Gaussian distribution’s center has been shifted to the origin. Once the optimization finished, ellipsoids will be reverted to the world space for rasterization.
The front fraction is omitted as the integral (“volume”) of 3D Gaussian isn’t limited to 1 to be a probability distribution, and considering a 3D Gaussian can be any size.
(2024-05-15)
- seh_sjij 解释为: 系数$\frac{1}{(2π)^{\frac{3}{2}}|Σ|^½}$被包含到了 opacity 中,然后 opacity 会自己优化。 CSDN
-
𝐀 is for rotating and stretching an ellipsoid. Thus, 𝐀=𝐑𝐒. And then 𝚺 = 𝐑𝐒𝐒ᵀ𝐑ᵀ
-
The covariance matrix 𝚺 gets optimized during training, such that the shape and direction of ellipsoids get adjusted to fit the scene.
-
-
Optimization
-
3D Gaussian representation based on point cloud from SfM.
-
Each 3D Gaussian contains properties: 3D position (xyz), shape (transform matrix 𝐀), SH coeffs (color), opacity (α).
-
Optimize rotate matrix 𝐑 using Quaternion instead of 3×3 matrix
-
-
Point cloud optimization
-
Remove points whose opacity lower than threshold after a certain epochs;
-
High positional gradients are inferred as a point is hard to reconstruct the geometry. So, small Gaussian do clone (for faster training), while large Gaussian do split (for recovering bkg).
-
Reset opacity to 0 periodically to remove floater around camera
-
-
Tile-based rasterization.
- An image is split into 16×16 patches.
- Sorting 3D ellipses observed by a patch based on depth.
- Terminate alpha compositing on a pixel when opactiy reaches 1.
- Each tile has a CUDA block, and each pixel has a CUDA thread.
Read Notes
(2023-05-14)
Three elements:
- Based on sparse points (colmap) and 3D Gaussians representation
- Point cloud optimization
- Fast rendering algorithm with GPU sorting (tile-based rasterization)
How much meomery does the 1-5 million (1e6) Gaussians (for all scenes tested) cost?
- Comparing with Mip-NeRF360 of 8.6MB, 3DGS has 523MB after 7K iterations on dataset “Mip-NeRF360”.
Chinese translation: 3DGS笔记 - bo233的文章 - 知乎
Abs
(2023-10-29)
NVS based on radiance field without neural network.
- SfM point cloud and 3D Gaussian representation.
- Point cloud adjustment: add and remove based on gradients.
- Tile-based rasterizer leveraging depth and cuda.
Intro
-
Points cloud format is chosen for rasterization. Then, 3D Gaussian is chosen to make point cloud a continuous field.
-
Efficient method based on continuous representation (MLP) most performed interpolation.
-
Neural nets representation is convinent to be optimized, but hinder fast rendering.
Related Works
-
Splatting made point-based rendering more efficient by extending the rasterization beyond a single pixel to cover a spread-out area.
-
Some methods used CNN to render.
-
NeRF requires extensive sampling around the entire space.
-
Pulsar is “order-independent”, whereas alpha-blending for a pixel is performed based on visibility order.
-
diffuse - diffusion model
Overview
-
The key to the efficiency of our method is our tile-based rasterizer.
-
Explicit scene representation appeals fast rendering without inferencing neural network.
-
Gradients are backpropagated to concrete 3D Gaussian.
-
Differentiable 3DGS
-
“Unstructured” is opposite to “regular volume grid”. 3DGS is unstructured but able to do volume rendering. Point cloud data + 3DGS primitive -> scene representation
-
Comparing with small planar circle representation for each point, 3D Gaussian doesn’t need normal. And normals are intractable for a sparse (SfM) point cloud.
-
covariance matrices have physical meaning only when they are positive semi-definite
Thus, they use a decomposed, equivalent form: 𝚺 = 𝐑𝐒𝐒ᵀ𝐑ᵀ , i.e., stretching and rotating an ellipsoid.
- Scaling matrix 𝐒 is represented by a 3D vector;
- Rotation 𝐑 is represented by a quaternion.
- Reparameterization is changing spaces. For example, spherical coords (θ,φ) of viewdir is recombinded to cartisian coords (x,y,z) in NeRF’s code. However, SVD doesn’t alter the number of dimensions, as a single space is split into 2 spaces.
(2024-07-09)
-
3DGS 中优化高斯分布的协方差矩阵时,将其分解成了 scaling 和 rotation 两个矩阵,这样做是因为直接优化协方差矩阵很难收敛吗? (文中说梯度下降无法保持协方差矩阵的半正定性质。) 不好优化是因为约束不够(?),“先分解再合成”就相当于是增加了额外的约束吗?
-
让我想起 TensoRF 先做了 tensor decomposition:把一个三维场景分解成 3 个一维向量(CP)或者 1 个向量加 1 个平面(VM), 再去优化各个 basis (component) 的 basic vector/plane
“把多个 pattern 叠加起来"就是重建,那 volume rendering 不也是这个意思?像素射线上的每个点是一个 component。 3DGS 是把相机射线上的椭球叠加起来,那一个椭球就是这个像素的component。
-
Optimization
-
Create, delete or move points (3D Gaussian) to fit geometry.
The quality of covariance of 3D Gaussians is critical for the compactness.
-
SGD performed by CUDA. Alpha comes from sigmoid. Covariance has done exponential activation.
The fast rasterization is critical in the efficiency of our optimization.
-
Loss function: 𝓛 = (1-λ)𝓛₁ + λ𝓛_dssim
-
Since the output is a complete image, SSIM is measured holistically between the gt image and predicted image. In contrast, S3IM is for random-ray patches.
-
Use absolute error of rgbs, instead of MSE.
-
Adaptive Density Control
-
Densify to better represent scene and remove transparent 3D Gaussians (points) every 100 iterations.
-
Total volume?
-
Reset alpha value close to zero every 3k iterations to reduce floaters near cameras.
Tile-based Gaussian
-
Split image into 16x16 patches ➔ Cull 3D Gaussians intersected with frustum ➔ Project 3D Gaussians to 2D ➔ Assign depth observed by a patch to each 3D Gaussian ➔ Sorting Gaussians based on depth for each patch.
-
A block is assigned to a patch and loads packets of Gaussians into shared memory.
Each pixel has a thread to do alpha compositing.
-
Reuse the per-tile lists for each pixel in the tile.
Implementation
-
Central-object photos taken from the entire hemisphere without angular regions missing result in good SH coefficients.
However, for incomplete observation, e.g., corners or “inside-out” photos, the 0th order SH prone to be corrupt during optimization.
So they first optimize only the 0-order coefficient for 1K iterations, then add 1 more coeff every 1K iters until all 4 orders are supplemented.
Results
- As fast as instantNGP, and as good as MipNeRF360.
- Synthetic dataset can use 100K random intialized point cloud in the bbox.
- More compact than other point-based methods.
Limitations
-
Hight memory cost due to point cloud representation. Tradeoff of model size for speed.
- Compress point cloud.
-
Defects occurs in the scene not well observed.
Play
(2023-11-01)
Environment
Ubuntu 18.04
Lambda Server: nvcc 10.2, Ubuntu 18.04, driver 470.103.01 with support for CUDA 11.4 at highest.
-
Clone needs –recursive:
git clone https://github.com/graphdeco-inria/gaussian-splatting --recursiveOtherwise, there will be an error when running
conda env create --file environment.yml:1ERROR: Directory 'submodules/diff-gaussian-rasterization' is not installable. Neither 'setup.py' nor 'pyproject.toml' found.Or fetch and install submodules individually:
1 2 3 4conda activate gaussian_splatting git submodule update --init --recursive pip install submodules/diff-gaussian-rasterization pip install submodules/simple-knn
-
Submodule install error:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19Pip subprocess error: error: subprocess-exited-with-error × python setup.py egg_info did not run successfully. │ exit code: 1 ╰─> [12 lines of output] Traceback (most recent call last): File "<string>", line 36, in <module> File "<pip-setuptools-caller>", line 34, in <module> File "/home/z/Downloads/gaussian-splatting/submodules/diff-gaussian-rasterization/setup.py", line 13, in <module> from torch.utils.cpp_extension import CUDAExtension, BuildExtension File "/home/z/anaconda3/envs/gaussian_splatting/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/__init__.py", line 201, in <module> _load_global_deps() File "/home/z/anaconda3/envs/gaussian_splatting/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/__init__.py", line 154, in _load_global_deps ctypes.CDLL(lib_path, mode=ctypes.RTLD_GLOBAL) File "/home/z/anaconda3/envs/gaussian_splatting/lib/python3.7/ctypes/__init__.py", line 364, in __init__ self._handle = _dlopen(self._name, mode) OSError: /home/z/anaconda3/envs/gaussian_splatting/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/lib/../../../../libcublas.so.11: symbol cublasLtGetStatusString version libcublasLt.so.11 not defined in file libcublasLt.so.11 with link time reference [end of output]-
Submodules (“diff-gaussian-rasterization”) needs compilation locally with CUDA Toolkit. issue#45
-
Alternative steps refer to issue#406
(2024-04-05)
I previously thought that the driver 470 is insufficient to install cuda 11.6, but I found that driver 470 is able to install CUDA 11.x on Docs. However, the problem persists when using cuda 11.6.
-
The problem is that my PATH has been modified previously. I once added a line in my .bashrc:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/home/z/anaconda3/envs/GNT/libThis caused the libcublas points to mismatched library. Refer to the answer of eval
I remove that line, and having the nvidia-driver 470 + ctk 11.6 on ubuntu 18.04, the env installation succeeds with just one line:
conda env create --file environment.ymlHe said by setting env virable
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=<anaconda dir>/python3.7/site-packages/torch/lib/nvidia/cublas/lib/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATHSo that “the dlopen will firstly look for .so files in that directory.” (I didn’t try that at present.)
-
-
Submodules compile error:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30/usr/local/cuda/bin/nvcc -I/home/z/anaconda3/envs/3dgs/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/include -I/home/z/anaconda3/envs/3dgs/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/include/torch/csrc/api/include -I/home/z/anaconda3/envs/3dgs/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/include/TH -I/home/z/anaconda3/envs/3dgs/lib/python3.9/site-packages/torch/include/THC -I/usr/local/cuda/include -I/home/z/anaconda3/envs/3dgs/include/python3.9 -c cuda_rasterizer/backward.cu -o build/temp.linux-x86_64-cpython-39/cuda_rasterizer/backward.o -D__CUDA_NO_HALF_OPERATORS__ -D__CUDA_NO_HALF_CONVERSIONS__ -D__CUDA_NO_BFLOAT16_CONVERSIONS__ -D__CUDA_NO_HALF2_OPERATORS__ --expt-relaxed-constexpr --compiler-options '-fPIC' -I/home/z/Downloads/gaussian-splatting/submodules/diff-gaussian-rasterization/third_party/glm/ -DTORCH_API_INCLUDE_EXTENSION_H -DPYBIND11_COMPILER_TYPE=\"_gcc\" -DPYBIND11_STDLIB=\"_libstdcpp\" -DPYBIND11_BUILD_ABI=\"_cxxabi1011\" -DTORCH_EXTENSION_NAME=_C -D_GLIBCXX_USE_CXX11_ABI=0 -gencode=arch=compute_61,code=compute_61 -gencode=arch=compute_61,code=sm_61 -std=c++14 cuda_rasterizer/backward.cu:15:10: fatal error: cooperative_groups/reduce.h: No such file or directory #include <cooperative_groups/reduce.h> ^~~------------------------- compilation terminated. ERROR: Could not build wheels for diff-gaussian-rasterization, which is required to install pyproject.toml-based projectsAnd compiling simple_knn.h will encounter:
1 2simple_knn.cu:17:10: fatal error: cub/cub.cuh: No such file or directory #include <cub/cub.cuh>-
Possible method: Add cub to CmakeLists.txt.Nvidia-forum -
nvcc mismatch and maybe 10.2 doesn’t have that function yet.
-
Ubuntu 20.04
-
Install new cudatookit on Alien PC (Ubuntu 20.04) CUDA Toolkit 12.3 Downloads | NVIDIA Developer
1 2 3 4 5 6 7wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu2004/x86_64/cuda-ubuntu2004.pin sudo mv cuda-ubuntu2004.pin /etc/apt/preferences.d/cuda-repository-pin-600 wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/12.3.0/local_installers/cuda-repo-ubuntu2004-12-3-local_12.3.0-545.23.06-1_amd64.deb sudo dpkg -i cuda-repo-ubuntu2004-12-3-local_12.3.0-545.23.06-1_amd64.deb sudo cp /var/cuda-repo-ubuntu2004-12-3-local/cuda-*-keyring.gpg /usr/share/keyrings/ sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get -y install cuda-toolkit-12-3Install driver:
1 2sudo apt-get install -y cuda-drivers # reboot is requiredBut
nvcc -Vstill returns 10.2. -
I found there are multiple “cuda” on my Alien PC. Nv-Install Guide Linux
-
Under dir “/usr/local/”, there are “cuda/”, “cuda11/”, “cuda11.6/”, “cuda12/”, “cuda12.3/”.
Only one could be used. SO. And the default version may can be checked by:
update-alternatives --display cudaDocs-Nv -
Add 11.6 to PATH:
1 2 3export PATH=/usr/local/cuda-11.6/bin${PATH:+:${PATH}} export CUDADIR=/usr/local/cuda-11.6 export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/cuda-11.6/lib64Then
nvcc -Vchange to 11.6. -
Success to create env on Alien PC with just the one line:
conda env create --file environment.yml -
For Lambda Server, although there is “cuda-11.2” folder in “/usr/local/”, but “bin/” doesn’t exist inside, so it can’t be added into PATH.
Therefore, the full cudatoolkit 11.6 and compatible driver (as above) are required, instead of the subset cudatoolkit for runtime installed by conda.
-
Ubuntu 22.04
(2023-11-03)
- CUDA Toolkit 11.6 doesn’t have version for Ubuntu 22.04
- CUDA Toolkit 11.8 corresponds PyTorch which is higher than 2.0.0
|
|
SIBR viewer install fails (Ubuntu 22.04) #151
(2024-05-17)
-
The
glmmodule missed because I forgot add--recursive(when cloning submoduledepth-diff-gaussian-rasterizationsolely:git submodule update --init --recursive). And the error about pyproject appears either:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11Compiling objects... - - - - - In file included from /home/zichen/Downloads/CasMVSNet_pl-comments/_3DGS/submodules/depth-diff-gaussian-rasterization/cuda_rasterizer/backward.cu:12: /home/zichen/Downloads/CasMVSNet_pl-comments/_3DGS/submodules/depth-diff-gaussian-rasterization/cuda_rasterizer/backward.h:19:10: fatal error: glm/glm.hpp: No such file or directory 19 | #include <glm/glm.hpp> | ^~-~-~-~-~-~-~-~-~-~-~-~ compilation terminated. - - - - - ERROR: Could not build wheels for diff_gaussian_rasterization, which is required to install pyproject.toml-based projects
Train
-
NeRF Synthetic
1python train.py -s ../nerf/data/nerf_synthetic/lego -r 8
DTU
(2024-04-15)
Train with DTU dataset:
-
Install Colmap.
To get the CUDA support on Linux, a local compilation is required. Docs
-
Use COLMAP to prepare training dataset with convert.py:
(2024-05-26)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9zichen@homepc:~/Downloads/gaussian-splatting$ tree . ├── convert.py ⋮ └── DTU_scan1 └─── input ├── 00000000.jpg ├── 00000002.jpg └── 00000004.jpgExecute:
1python convert.py -s DTU_scan1The generated point cloud is a binary file:
sparse/0/points3D.bin, which will be read withread_points3D_binary(). -
Train:
1(3dgs) zichen@homepc:~/Downloads/gaussian-splatting$ python train.py -s DTU_scan1 -
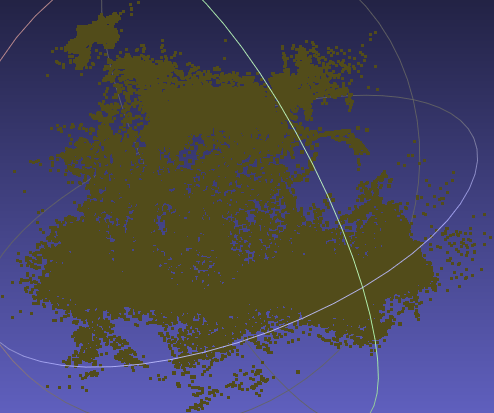
The result point cloud doesn’t perserve a good geometry:
input.ply iter30K 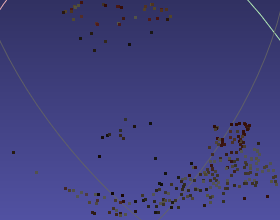
 >}}
>}}-
Given 3 views, COLMAP produced very sparse points.
-
The gaussian clone and split maybe not accurate enough for recovering the geometry.
-
T&T
(2024-05-26)
Ref:
Steps:
-
Use COLMAP to estimate camera poses from input images:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9zichen@homepc:~/Downloads/gaussian-splatting$ tree . ├── convert.py ⋮ └── TnT_Barn └─── input ├── 000010.jpg ├── 000179.jpg └── 000184.jpgExecute:
1python convert.py -s TnT_Barn --resize- I removed the
magick_commandvariable when constructing commands (at L105, L112, L119):exit_code = os.system(" mogrify -resize 50% " + destination_file)as Ubuntu 22.04 doesn’t havemagick.
- I removed the
-
Train:
1(3dgs) zichen@homepc:~/Downloads/gaussian-splatting$ python train.py -s TnT_Barn -
Result model of Barn with 2 views (
010.jpgand184.jpg) input:
- As Pixel-GS descriped (in abstract): there are lots of “needle-like artifacts”.
SIBR viewer
Ubuntu 20.04
On Ubuntu 20.04, 1050Ti:
|
|
Some details:
-
Install cmake by compiling source code:
Download tar.gz (cmake-
.tar.gz), such as cmake-3.29.1.tar.gz, and extract: tar -zxvf cmake-{version number}.tar.gz1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13# Dependecy for OpenSSL sudo apt-get install libssl-dev cd cmake-{version number} # Check required dependencies: ./bootstrap # Build package: make # Install sudo make install cmake --versionRef How to Install CMake on Ubuntu 22.04 or 20.04 - LinuxCapable
-
OpenCV issue on Ubuntu 20.04 resolved by switching branch to “fossa_compatibility”. Installing SIBR - cannot find correct version of OpenCV #10
-
sm_30 error
With cudatoolkit 11.6 added to PATH, an error occurs:
1 2 3 4#$ ptxas -arch=sm_30 -m64 "tmp/CMakeCUDACompilerId.ptx" -o "tmp/CMakeCUDACompilerId.sm_30.cubin" ptxas fatal : Value 'sm_30' is not defined for option 'gpu-name'-
Check if old-version cuda exists:
apt-cache policy nvidia-cuda-toolkit. 【已解决】 Compilation error ptxas fatal :1 2 3 4 5 6 7nvidia-cuda-toolkit: Installed: 10.1.243-3 Candidate: 10.1.243-3 Version table: *** 10.1.243-3 500 500 http://ca.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/multiverse amd64 Packages 100 /var/lib/dpkg/statusRemove it:
sudo apt remove nvidia-cuda-toolkitThen, re-build works.
-
-
Run local viewer
1./SIBR_viewers/install/bin/SIBR_gaussianViewer_app -m output/c777580e-9Error (Real-time viewer requires CC > 7.0):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18(gaussian_splatting) yi@yi-Alienware-Aurora-R8:~/Downloads/gaussian-splatting$ ./SIBR_viewers/install/bin/SIBR_gaussianViewer_app -m output/c777580e-9/ --no_interop [SIBR] -- INFOS --: Initialization of GLFW [SIBR] -- INFOS --: OpenGL Version: 4.6.0 NVIDIA 545.23.06[major: 4, minor: 6] Number of input Images to read: 300 Number of Cameras set up: 300 [SIBR] -- INFOS --: Error: can't load mesh '/home/yi/Downloads/nerf/data/nerf_synthetic/lego. [SIBR] -- INFOS --: Error: can't load mesh '/home/yi/Downloads/nerf/data/nerf_synthetic/lego.ply. [SIBR] -- INFOS --: Error: can't load mesh '/home/yi/Downloads/nerf/data/nerf_synthetic/lego.obj. LOADSFM: Try to open /home/yi/Downloads/nerf/data/nerf_synthetic/legopoints3D.bin [SIBR] -- INFOS --: Error: can't load mesh '/home/yi/Downloads/nerf/data/nerf_synthetic/legopoints3D.bin. [SIBR] !! WARNING !!: FILE /home/yi/Downloads/gaussian-splatting/SIBR_viewers/src/core/scene/ProxyMesh.cpp LINE 29, FUNC loadFromData proxy model not found at /home/yi/Downloads/nerf/data/nerf_synthetic/lego [SIBR] ## ERROR ##: FILE /home/yi/Downloads/gaussian-splatting/SIBR_viewers/src/projects/gaussianviewer/renderer/GaussianView.cpp LINE 339, FUNC GaussianView Sorry, need at least compute capability 7.0+!terminate called after throwing an instance of 'std::runtime_error' what(): See log for message errors Aborted (core dumped)- Even the 1080 Ti’s compute capacity is only 6.1 ? Your GPU Compute Capability
Ubuntu 22.04
(2023-11-04)
Install:
|
|
Train: python train.py -s ../Dataset/nerf_synthetic/lego
Real-time viewer: sudo ./SIBR_viewers/install/bin/SIBR_gaussianViewer_app -m output/4ee28b3c-9
Run Network viewer:
|
|
(2024-05-09)
-
Use SIBR to view the trained model with point cloud initialization from CasMVSNet
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16(3dgs) zichen@homepc:~/Downloads/gaussian-splatting$ ./SIBR_viewers/install/bin/SIBR_gaussianViewer_app -m ../CasMVSNet_pl-comments/output/no_densify_0509/ ./SIBR_viewers/install/bin/SIBR_gaussianViewer_app: error while loading shared libraries: libassimp.so.5: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory (3dgs) zichen@homepc:~/Downloads/gaussian-splatting$ sudo apt install -y libglew-dev libassimp-dev libboost-all-dev libgtk-3-dev libopencv-dev libglfw3-dev libavdevice-dev libavcodec-dev libeigen3-dev libxxf86vm-dev libembree-dev 有一些软件包无法被安装。如果您用的是 unstable 发行版,这也许是 因为系统无法达到您要求的状态造成的。该版本中可能会有一些您需要的软件 包尚未被创建或是它们已被从新到(Incoming)目录移出。 下列信息可能会对解决问题有所帮助: 下列软件包有未满足的依赖关系: libminizip-dev : 依赖: libminizip1 (= 1.1-8build1) 但是 1.1.1-1+rebuild 正要被安装 E: 无法修正错误,因为您要求某些软件包保持现状,就是它们破坏了软件包间的依赖关系。 (3dgs) zichen@homepc:~/Downloads/gaussian-splatting$ sudo aptitude install -y libglew-dev libassimp-dev libboost-all-dev libgtk-3-dev libopencv-dev libglfw3-dev libavdevice-dev libavcodec-dev libeigen3-dev libxxf86vm-dev libembree-dev (3dgs) zichen@homepc:~/Downloads/gaussian-splatting$ ./SIBR_viewers/install/bin/SIBR_gaussianViewer_app -m ../CasMVSNet_pl-comments/output/no_densify_0509/Then, it works:
Ubuntu 18.04
(2024-04-05)
The current cmake on server is 3.10, which is too old.
-
Using the pre-built cmake cmake-3.29.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz will lead to error.
1 2 3 4 5 6wget https://github.com/Kitware/CMake/releases/download/v3.29.1/cmake-3.29.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz tar -zxvf cmake-3.29.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz # Build SIBR cd ./Downloads/gaussian-splatting/SIBR_viewers /home/z/Downloads/cmake-3.29.1-linux-x86_64/bin/cmake -Bbuild . -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=ReleaseError
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8CMake Error at /home/z/Downloads/cmake-3.29.1-linux-x86_64/share/cmake-3.29/Modules/FindPackageHandleStandardArgs.cmake:230 (message): Could NOT find GLEW (missing: GLEW_INCLUDE_DIRS GLEW_LIBRARIES) Call Stack (most recent call first): /home/z/Downloads/cmake-3.29.1-linux-x86_64/share/cmake-3.29/Modules/FindPackageHandleStandardArgs.cmake:600 (_FPHSA_FAILURE_MESSAGE) /home/z/Downloads/cmake-3.29.1-linux-x86_64/share/cmake-3.29/Modules/FindGLEW.cmake:242 (find_package_handle_standard_args) cmake/linux/dependencies.cmake:69 (FIND_PACKAGE) cmake/linux/include_once.cmake:20 (include) src/CMakeLists.txt:46 (include_once) -
Using local
cmaketo compile remote folder, which is mounted via sshfs doesn’t work neither:1 2 3 4(base) yi@yi:/mnt/Server/Downloads/gaussian-splatting/SIBR_viewers$ cmake -Bbuild . -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release CMake Error: The current CMakeCache.txt directory /mnt/Server/Downloads/gaussian-splatting/SIBR_viewers/CMakeCache.txt is different than the directory /home/z/Downloads/gaussian-splatting/SIBR_viewers where CMakeCache.txt was created. This may result in binaries being created in the wrong place. If you are not sure, reedit the CMakeCache.txt -
Clone the CMake repo and build it.
git clone https://github.com/Kitware/CMake.gitInstall lib for ssl:
sudo apt-get install libssl-devto avoid SSL error:1 2 3 4-- Could NOT find OpenSSL, try to set the path to OpenSSL root folder in the system variable OPENSSL_ROOT_DIR (missing: OPENSSL_CRYPTO_LIBRARY OPENSSL_INCLUDE_DIR) CMake Error at Utilities/cmcurl/CMakeLists.txt:644 (message): Could not find OpenSSL. Install an OpenSSL development package or configure CMake with -DCMAKE_USE_OPENSSL=OFF to build without OpenSSL.1 2 3cd CMake/ mkdir build && cd build ../bootstrap && makeThe using cmake to compile project:
1 2cd ~/Downloads/gaussian-splatting/SIBR_viewers ../../CMake/build/bin/cmake -Bbuild . -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=ReleaseBut this still encounters the same error as above.
1 2CMake Error at /home/z/Downloads/CMake/Modules/FindPackageHandleStandardArgs.cmake:230 (message): Could NOT find GLEW (missing: GLEW_INCLUDE_DIRS GLEW_LIBRARIES)Copy the compiled executable files onto system.
1 2cd sudo make installCmake 3.29 gets installed (copied) into:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11/usr/local/doc/cmake-3.29/cmsys/Copyright.txt ... ... ... -- Installing: /usr/local/share/cmake-3.29/Modules/ ... -- Installing: /usr/local/share/cmake-3.29/Templates ... -- Installing: /usr/local/share/vim/vimfiles/indent ... -- Installing: /usr/local/share/emacs/site-lisp/cmake-mode.el -- Installing: /usr/local/share/aclocal/cmake.m4 -- Installing: /usr/local/share/bash-completion/completions/Relaunch a terminal. Check the version:
1 2 3 4(base) z@lambda-server:~/Downloads/gaussian-splatting$ cmake --version cmake version 3.29.20240405-gc2949db CMake suite maintained and supported by Kitware (kitware.com/cmake).Build SIBR:
1 2 3 4 5git checkout fossa_compatibility git checkout master cd SIBR_viewers cmake -Bbuild . -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=ReleaseThe error persists!! as below: (Note: The following error corresponds to the
masterbranch.)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8CMake Error at /usr/local/share/cmake-3.29/Modules/FindPackageHandleStandardArgs.cmake:230 (message): Could NOT find GLEW (missing: GLEW_INCLUDE_DIRS GLEW_LIBRARIES) Call Stack (most recent call first): /usr/local/share/cmake-3.29/Modules/FindPackageHandleStandardArgs.cmake:600 (_FPHSA_FAILURE_MESSAGE) /usr/local/share/cmake-3.29/Modules/FindGLEW.cmake:245 (find_package_handle_standard_args) cmake/linux/dependencies.cmake:69 (FIND_PACKAGE) cmake/linux/include_once.cmake:20 (include) src/CMakeLists.txt:46 (include_once)Install dependencies:
1sudo apt install -y libglew-dev libassimp-dev libboost-all-dev libgtk-3-dev libopencv-dev libglfw3-dev libavdevice-dev libavcodec-dev libeigen3-dev libxxf86vm-dev # libembree-devIt prompts that
E: Unable to locate package ibembree-dev.Then, the building will prompts error about libboost:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10CMake Error at /usr/local/share/cmake-3.29/Modules/FindPackageHandleStandardArgs.cmake:230 (message): Could NOT find Boost: Found unsuitable version "1.65.1", but required is at least "1.71.0" (found /usr/include, found components: system chrono filesystem date_time) Call Stack (most recent call first): /usr/local/share/cmake-3.29/Modules/FindPackageHandleStandardArgs.cmake:598 (_FPHSA_FAILURE_MESSAGE) /usr/local/share/cmake-3.29/Modules/FindBoost.cmake:2394 (find_package_handle_standard_args) cmake/dependencies.cmake:173 (find_package) cmake/include_once.cmake:20 (include) src/CMakeLists.txt:46 (include_once)The header and libraries of libboost are in:
1 2 3-- Found Boost: /usr/include (found version "1.65.1") -- Boost_INCLUDE_DIRS: /usr/include -- Boost_LIBRARY_DIRS: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnuThese information is return by adding command into CMakeLists.txt (guided by chatGPT):
1 2 3find_package(Boost REQUIRED) message(STATUS "Boost_INCLUDE_DIRS: ${Boost_INCLUDE_DIRS}") message(STATUS "Boost_LIBRARY_DIRS: ${Boost_LIBRARY_DIRS}")I don’t know how to update libboost.
I found the CMakeLists.txt varies between different branch.
The branch of SIBR used by 3DGS is
gaussian_code_release_union(4ae964a267):1 2 3git checkout gaussian_code_release_union cd SIBR_viewers cmake -Bbuild . -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=ReleaseWarnings about embree, and errors for OpenCV4.5:
Error
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33# Warnings CMake Warning at cmake/linux/dependencies.cmake:127 (find_package): By not providing "Findembree.cmake" in CMAKE_MODULE_PATH this project has asked CMake to find a package configuration file provided by "embree", but CMake did not find one. Could not find a package configuration file provided by "embree" (requested version 3.0) with any of the following names: embreeConfig.cmake embree-config.cmake Add the installation prefix of "embree" to CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH or set "embree_DIR" to a directory containing one of the above files. If "embree" provides a separate development package or SDK, be sure it has been installed. Call Stack (most recent call first): cmake/linux/include_once.cmake:20 (include) src/CMakeLists.txt:46 (include_once) # Errors: There is no provided OpenCV library for your compiler, relying on find_package to find it CMake Error at cmake/linux/dependencies.cmake:248 (find_package): Could not find a configuration file for package "OpenCV" that is compatible with requested version "4.5". The following configuration files were considered but not accepted: /usr/share/OpenCV/OpenCVConfig.cmake, version: 3.2.0 Call Stack (most recent call first): cmake/linux/include_once.cmake:20 (include) src/CMakeLists.txt:46 (include_once)Then I change to branch
fossa_compatibility:1 2 3git checkout fossa_compatibility cd SIBR_viewers cmake -Bbuild . -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=ReleaseThe error of OpenCV4 occurs:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25CMake Warning (dev) at /usr/local/share/cmake-3.29/Modules/FindPackageHandleStandardArgs.cmake:438 (message): The package name passed to `find_package_handle_standard_args` (EMBREE) does not match the name of the calling package (embree). This can lead to problems in calling code that expects `find_package` result variables (e.g., `_FOUND`) to follow a certain pattern. Call Stack (most recent call first): cmake/linux/Modules/Findembree.cmake:87 (FIND_PACKAGE_HANDLE_STANDARD_ARGS) cmake/linux/dependencies.cmake:127 (find_package) cmake/linux/include_once.cmake:20 (include) src/CMakeLists.txt:46 (include_once) This warning is for project developers. Use -Wno-dev to suppress it. -- EMBREE wasn't found correctly. Set EMBREE_DIR to the root SDK installation directory. (missing: EMBREE_INCLUDE_DIR EMBREE_LIBRARIES) There is no provided OpenCV library for your compiler, relying on find_package to find it CMake Error at cmake/linux/dependencies.cmake:248 (find_package): Could not find a configuration file for package "OpenCV" that is compatible with requested version "4". The following configuration files were considered but not accepted: /usr/share/OpenCV/OpenCVConfig.cmake, version: 3.2.0 Call Stack (most recent call first): cmake/linux/include_once.cmake:20 (include) src/CMakeLists.txt:46 (include_once)Authors said the SIBR has no support for Ubuntu 18. Related issues with searching “18.04”