Table of contents
3D Transformations
3D Scale
$$ \mathbf S(s_x, s_y, s_z) = \begin{pmatrix} s_x & 0 & 0 & 0 \\\ 0 & s_y & 0 & 0 \\\ 0 & 0 & s_z & 0 \\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} $$3D Translation
$$ \mathbf T(t_x,t_y,t_z) = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & t_x \\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & t_y \\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & t_z \\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} $$Rotaion around axises
-
绕x轴旋转:
x方向坐标不变,所以旋转矩阵各列向量的x分量都不贡献,所以第一行是1 0 0;
为了保证逆时针旋转是正向旋转,其余两轴的顺序如图: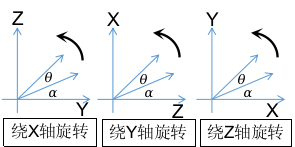
y-z平面旋转,用待定系数法或展开三角函数,可得旋转关系为: $\begin{cases} x'=x \\\\ y'=ycosθ-zsinθ \\\\ z'=ysinθ+zcosθ \end{cases}$,
$$ R_x(α)= \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\\ 0 & cosθ & -sinθ & 0 \\\ 0 & sinθ & cosθ & 0 \\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\\ \end{pmatrix} $$
则旋转矩阵为 $\begin{pmatrix} x' \\\\ y' \\\\ z' \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 1&0&0\\\\ 0 & cosθ & -sinθ \\\\0 & sinθ & cosθ \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} x\\\\y\\\\z\end{pmatrix}$;
写成齐次坐标,不考虑平移,所以仿射变换矩阵为: -
绕y轴旋转:
$$ \begin{pmatrix} x' \\\ y' \\\ z' \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} cosθ & 0 & sinθ \\\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\\ -sinθ & 0 & cosθ \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} x \\\ y \\\ z \end{pmatrix} $$
y方向不变,所以矩阵第2行为:0 1 0;
x-z平面旋转,用待定系数法,可得旋转关系: $\begin{pmatrix}z'\\\\x' \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix}cosθ& -sinθ\\\\sinθ & cosθ\end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} z\\\\x \end{pmatrix}$
(或者展开三角函数,可得旋转关系为: $\begin{cases} x'=zsinθ+xcosθ \\\\ z'=zcosθ-xsinθ\end{cases}$)
写成旋转矩阵为:三个轴循环对称:$x\boxed{yzx}y\boxed{zxy}z\boxed{xyz}$,即给定任意两个可得后面一个,所以Y是由$Z×X$的到的 $\begin{pmatrix}Z\\\\ X\\\\ Y\end{pmatrix}$,这与通常书写 矩阵顺序$\begin{pmatrix}X\\\\ Y\\\\ Z\end{pmatrix}$不同,导致系数易位,$-sinθ$不在左上角,看起来与绕其他两轴的旋转矩阵不一致。
-
绕z轴旋转:
$$ \begin{pmatrix} x' \\\ y' \\\z' \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} cosθ & -sinθ & 0 \\\ sinθ & cosθ & 0 \\\ 0 & 0 & 1 \\\ \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} x \\\ y \\\z \end{pmatrix} $$
z方向不变,所以矩阵第3行为:0 0 1;
x-y平面旋转,有旋转关系 $\begin{cases}x'=rcos(α+θ)\\\\y'=rcos(α+θ)\end{cases}$ 以及 $\begin{cases}x=rcosα\\\\y=rsinα\end{cases}$
可得:$\begin{cases}x'=xcosθ-ysinθ\\\\y'=ycosθ+xsinθ\end{cases}$
写成旋转矩阵为:
任意三维旋转
渲染
- 给三维物体拍照片
-
- 摆好模型 Model transformation
- 摆好照相机 View transformation
- 投影到相片 Projection transformation
View Transformation
-
通过旋转和平移,把世界坐标系中的相机调整到标准姿态
-
相机的姿态包括:位置、朝向和旋转
标准姿态:
- 光心在原点;
- 朝着-z方向看;
- 向上是y轴
-
从标准姿态变换到当前姿态,再取逆,就是视图变换
正交投影
- 平行光
- 把空间中的长方体映射到一个边长为2的立方体(左右下上远近的边界都是1)
- 中心平移到原点: $\begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & -\frac{r+l}{2} \\\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & -\frac{t+b}{2} \\\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & -\frac{n+f}{2} \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}$
- 缩放到2: $\begin{pmatrix}\frac{2}{r-l} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 0 & \frac{2}{t-b} & 0 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & \frac{2}{n-f} & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\end{pmatrix}$
透视投影
- 视锥
- 近大远小
- 把棱台挤压成长方体,长方体再做正交投影
-
远平面缩放到与近平面相同大小
根据相似,确定不同深度的缩放系数
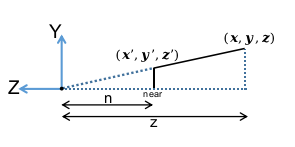 $$
\begin{cases}
y'=\frac{n}{z}y \\\
x'=\frac{n}{z}x \\\
z'=unknow
\end{cases}
$$
$$
\begin{cases}
y'=\frac{n}{z}y \\\
x'=\frac{n}{z}x \\\
z'=unknow
\end{cases}
$$远平面缩放之后各点坐标:
$$ \begin{pmatrix} \frac{nx}{z} \\\ \frac{ny}{z} \\\ unknown \\\ 1 \end{pmatrix} \overset{乘以深度z}{==} \begin{pmatrix} nx \\\ ny \\\ unkown \\\ z \end{pmatrix} $$ -
确定$M\_{persp→ortho}$
$$ M\_{persp→ortho}^{(4×4)} \begin{pmatrix} x \\\ y \\\ z \\\ 1 \end{pmatrix}= \begin{pmatrix} nx \\\ ny \\\ unknown \\\ z \end{pmatrix} $$$$ M_{persp→ortho}^{(4×4)} = \begin{pmatrix} n & 0 & 0 & 0 \\\ 0 & n & 0 & 0 \\\ ? & ? & ? & ? \\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\ \end{pmatrix} $$近平面上的点作用之后不变:
$$ \begin{pmatrix} n & 0 & 0 & 0 \\\ 0 & n & 0 & 0 \\\ ? & ? & ? & ? \\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\ \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} x \\\ y \\\ n \\\ 1 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} x \\\ y \\\ n \\\ 1 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} nx \\\ ny \\\ n^2 \\\ n \end{pmatrix} $$因为$n^2$与x,y无关,所以第三行为:(0 0 A B), $An+B=n^2$
远平面的中心点也没变,满足:
$$ \begin{pmatrix} n & 0 & 0 & 0 \\\ 0 & n & 0 & 0 \\\ 0 & 0 & A & B \\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\ \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} 0 \\\ 0 \\\ f \\\ 1 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 0 \\\ 0 \\\ f \\\ 1 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 0 \\\ 0 \\\ f^2 \\\ f \end{pmatrix} $$所以$Af+B=f^2$
联立可解得A,B:
$$ \begin{cases} An+B=n^2 \\\ Af+B=f^2 \end{cases} ⇒ \begin{cases} A=n+f \\\ B=-nf \end{cases} $$ -
透视投影矩阵:$M_{persp} = M_{ortho} M_{persp→ortho}$
-