Video 7 2021-10-04
[toc]
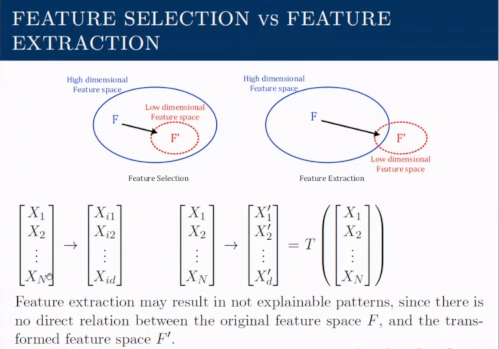
Dimensionality Reduction
- Avoids the curse of Dimensionality
October 6, 2021
Curse of Dimensionality
- When dimensionality increases, data becomes increasingly sparse
-
- Concepts become less meaningful: density and distance
- Subspace combinations grow very fast
Dimentionality Reduction
-
Eliminate irrelevant features and reduces noise
-
$X$ is a set of $N$ features: $X={X_1, X_2, \cdots X_N}$,a reduced set $X’$ is a transformation of $X$ and consists of $d$ features so that $d<N$:
$$ X’ = T(X) = { X_1’,\ X_2’,\ \cdots,\ X_d’} \ T: \R^N \rightarrow \R^d,\ d<N $$
-
Avoids the curse of dimensionality. Reduces time and space required for computations.>
-
Two ways:
- Feature Extraction: transformation to a lower dimension
- Wavelet transforms and PCA
- Feature Selection: transformation is limited to only selection from original features
- Filters, Wrappers, Embedded.
- Feature Extraction: transformation to a lower dimension
3 Features
- Relevant feature is neither irrelevant nor redundant to the target concept.
- Irrelevant feature is useless information for the learning task, and may causes greater computational cost and overfitting
- Redundant feature is duplication of information that has contained in other features.
Feature Selection
Assume a binary classification model, X → Model → Y ∈ {0, 1}, where X consists of N different features, e.g., age, weight, temperature, blood pressure, etc. X = {X1, X2, X3 , . . . , XN } N could be small, or relatively large value, e.g., an image of size of 300 × 300.
Class Separation Criterion
-
Evaluation of data separation result based on selected features.
-
$$ \begin{aligned} 变换 \quad & T: \R^N → \R^d, \quad d<N & \text{(把数据从N维降到d维)} \ 分离结果\quad & X’= T(X) \ 分离评价\quad & J(X’,Y) = 1-ε^* (X’,Y) & \text{(Y: class distribution; ε是X’与Y的误差)} \end{aligned} $$
-
根据最大化 J 或者最小化ε来设计h,实现更好的样本分离
Feature Selection
-
Find the optimal subset of d features $S^$ from N features, according to $S^ = \underset{|S|=d}{\operatorname{arg,max}}J(S)$
-
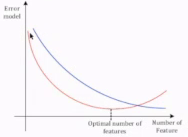
Optimal number of features bring lowest error of model
-
FS包括两部分: 搜索策略 Search Strategy 和 目标函数 Objective Function
- Search Strategy: 若 d 固定会有$C_d^N$次评价;若 d 也需优化,就有$2^N$次评价比较,为了在所有的特征组合之中搜索,需要一个搜索策略来引导。
- Objective Function: 量化特征子集的好坏,以供search strategy 判断
-
Importance:
- Reduce computational complexity, run-time, required storage.
- FS can get meaningful and explainable rules from model based on raw data with real meaning.
- Building better generalizable model. FS can be applied for non-numerical features, which cannot be transformed easily.
-
类分离评价标准:$J(X^S,Y) = J(S)$越大越好,由Bayes error, classifier error或Mahalanobis distance定义。误差越小,J越大。
Search Strategies
- Search sequence of N features
- Find the subset of d features from all possible combination of features quickly
- Three major categories:
-
Sequential algorithms: Add or remove features sequentially
Shortcoming: a tendency to become trapped in local minima
-
Exponential algorithms: Used to evaluate a number of subsets that grows exponentially with the dimensionality of the search space.
- Exhaustive Search
- Branch and Bound
- Approximate Monotonicity with a Branch and Bound
- Beam Search
-
Randomized algorithms: Incorporate randomness into search procedure to escape from local minima
- Random Generation plus Sequential Selection
-
Objective Function
- Evaluation of subset goodness
- 三大类:
- Filter Methods: statistical analysis without using predictive model statistical dependence, information gain, Chi square, log likelihood ratio, interclass distance or information-theoretic measures
- Wrapper Methods: pre-determined predictive models or classifiers
- Hybrid Methods: complement of wrapper and filter approaches
Filters Approaches
-
select d features greedy which are used for training a predictive model $h_M$ with M samples

$$ X^N \overset{FS}{\longrightarrow} X^d \overset{h_m}{\longrightarrow}Y $$
-
Why is it?
- Evaluation is independent of the predictive models or classifiers.
- Objective function evaluate the information content and statistical measures of feature subsets
-
Role: evaluate each feature individually or a batch of features
-
Major steps:
- Evaluating and ranking features
- Choosing the features with the highest ranks to induce models
-
Advantages:
- Fast Execution: non-iterative computation is faster than training session of predictive models
- Generality: evaluate intrinsic properties of the data, rather than their interactions with a particular predictive model. So the final subset is general for any subsequent predictive models
-
Disadvantages:
- Tendency to select large subsets: more features will make the monotonic objective functions larger
- Independence: ignore the performance on predictive models
Wrapper Approches
-
a predictive model $h_M$ is trained to find the best subset $S^*$

-
一个预测模型被包在了“选择系统”里面
-
Maximize the separation criterion J or minimize the estimiated error$\epsilon$
-
不采取穷尽搜索,而是搜索较少的特征空间,找到 sub-optimal 解。Evaluation 标准与 predictive models 和 classifiers 相关。通过在测试数据上验证准确性来评选特征子集。
-
Advantages:
- Accuracy: 因为更关注特定 predictive model 与数据之间的交互,所以要比 filter approaches 在预测结果上更准确。
- Generalization ability: 因为通常采取 cross-validation,所以可以避免过拟合
-
Disadvantages:
- Slow execution: 训练predictive model 花时间
- Lack of generality: 仅使用一个特定的predictive model
Best Individual Features
-
最佳个体特征:一个特征的单独分类效果好于其他特征单独作用的效果
-
$$ J_{i*} = \underset{i \in N}{\operatorname{arg\ max}} J(X_i, Y) $$
-
并不能保证组合起来的效果还是最好的
Sequential Forward Search
-
顺序前向搜素:第一个特征选最佳单体特征BIF,然后每次都取当前的最佳组合,选够d个特征,或者 J 出现下降,就是输出

-
最简单的贪心搜索算法 (the simplest greedy search algorithm)
-
适合挑选小容量的特征子集
-
Feature freeze: Once a feature added to the selection list can not be deleted. 所以不能保证最终结果是最好的
Sequential Backward Search
- 顺序后向搜索:从特征全集开始,顺序移除那个使$J(X_i,Y)$下降最小的特征,

- 适合挑选大容量的特征子集
- Limitation: 无法评价已经被移除特征的作用
General SFS and General SBS
-
广义顺序前向搜索:允许每次选中多个(r)特征,进行评估,添加或删除
-
减少判断次数
-
GSFS:

PLUS-L TAKE-R
-
加 L 减 R。In Plus-L Take away-R
-
If L>R: 从空集开始,先按SFS加入L个特征,再按SBS移除R个特征。
If L<R: 从全集开始,先按SBS移除R个特征,再按SFS加入L个特征
-
作用:attemps to compensate for the weaknesses of SFS and SBS with some backtracking capabilities (回溯能力)
-
Limitation: Lack of theory to help predict the optimal values of L and R.
-
例:从10个特征中选3个,L=3,R=2
3>2,所以从空集开始,先加3个特征,再移除2个特征

Sequential Floating Selection
-
顺序浮动选择:每次迭代时,可以调整 L 和 R
-
在PLTS的基础上,不固定L 和 R。
-
优化L和R
-
Two floating methods:
- Sequential Floating Forward Selection (SFFS) 顺序浮动前向选择
Starts from the empty set. After each forward step, SFFS performs backward steps as long as the objective function increases.
- Sequential Floating Backward Selection (SFBS) 顺序浮动后向选择
Starts from the full set. SFBS performs forward steps as long as the objective function increases