Difference between plt and fig,ax
object-oriented
Inverse the X-axis
|
|
Add caption below the x-label
-
1 2 3fig, ax = plt.subplots() txt = 'near and far are distance' fig.text(x=.5, y=.001, s=txt, ha='center')
|
|
微分柱形图

Set xticks
xticks is the (fixed) number on the x-axis, while xticklabels can be customized strings.
-
For plt (
Matplotlib.pyplot.xticks()): Matplotlib Set_xticks - Detailed Tutorial - Python Guides -
Matplotlib.axes.Axes.set_xticklabels()Matplotlib Set_xticklabels -Python Guides1 2 3fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.set_xticks([0, np.pi, 2*np.pi, 3*np.pi]) ax.set_xticklabels(labels=['0', r'$\pi$', r'2$\pi$', r'3$\pi$'], fontdict=None, fontsize=6, fontstyle='italic', color='red', verticalalignment='top', horizontalalignment='left', rotation=90, minor=True,
Change the number and text of the showing Ticks
-
For
plt:1 2plt.xticks(ticks=[1,2,3,4], labels=None, **kwargs) plt.yticks(ticks=[7,13,24,22], labels=None,) -
Use
locator_param()to change the tightness and number of ticks.plt.locator_params(axis='both', nbins=4) -
Use
xlim()to restrict the diplayed area, rather the whoel plot.1 2plt.xlim(0,3) plt.locator_params(axis='x', nbins=3) -
Use
Matplotlib.ticker.MaxNLocatorclass
Set Number of Ticks in Matplotlib | Delft Stack
|
|
Set y-axis view limits
Matplotlib.axes.Axes.set_ylim() in Python - GeeksforGeeks
|
|
Set the 1st x as 1 (not 0)
Python MatplotLib plot x-axis with first x-axis value labeled as 1 (instead of 0)
Add extra ticks and labels
-
Add extra ticks which must be number, not work for string SO
1 2 3fig, ax= plt.subplots() extraticks = [2.1, 3, 7.6] ax.set_xticks(list(ax.get_xticks()) + extraticks) -
Use
ax.set_xticklabels()for string Create label list - SO1 2 3 4 5near, far = 1, 15 ax.set_xticks(list(ax.get_xticks()) + [-near,-far]) # Their labels also have to be appended at the end. xticklabels= ['-16', '-14', '-12', '-10', '-8', '-6', '-4', '-2','0', '-near', '-far'] ax.set_xticklabels(xticklabels, rotation=90)
Example: Mark the yticks for the highest and lowest points:
|
|
Set xticks as integer
(Not sure) ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(MaxNLocator(integer=True))
-
Python:使用f-string保留小数点位数 csdn
-
用decimal 模块:w3cschool
1 2 3from decimal import Decimal a = 12.345 Decimal(a).quantize(Decimal("0.00")) # 使用默认的进位方式(同round)“0.00”表示保留小数点后两位
Margin
to leave more space around the figure to show the ticks of the boundary Geeksforgeeks
Or prevent the markers get clipped by the axes GfG plt xticks
|
|
Hide ticks
Legend
|
|
-
Put it below the subplots:
ax.legend(loc="upper center", bbox_to_anchor=(0.5, -0.13),fancybox=False, shadow=False, ncol=5, fontsize=6)
Draw a horizontal line
-
plt : gfg
1plt.axhline(y=0.5, color='r', linestyle='-') -
ax: SO
1ax.hlines(y=0.2, xmin=0.01, xmax=20, linewidth=2, color='r')
Tight layout
|
|
Or: plt.rcParams["savefig.bbox"] = 'tight'
Save as png
|
|
Draw markers on axes
plt.plot(x,y, zorder=10, clip_on=False)
plotting markers on top of axes
Arrow of axis
Change fonts
Plot in Ubuntu has ugly fonts (which is like ‘sans-serif’).
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "cursive",
This will change to your computer’s default monospace font.
How to change fonts in matplotlib (python)?
散点图
-
plt.scatter(x,y, c='r', s=4), s can control marker size, docs -
marker 是反着画的
-
matplotlib.pyplot.scatter(x, y, s=None, c=None, marker=None, cmap=None, norm=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, alpha=None, linewidths=None, verts=None, edgecolors=None, hold=None, data=None, **kwargs)
x,y组成了散点的坐标;s为散点的面积;c为散点的颜色(默认为蓝色’b’);marker为散点的标记;alpha为散点的透明度(0与1之间的数,0为完全透明,1为完全不透明);linewidths为散点边缘的线宽;如果marker为None,则使用verts的值构建散点标记;edgecolors为散点边缘颜色。 csdn
拉长坐标间距
Python设置matplotlib.plot的坐标轴刻度间隔以及刻度范围
|
|
设置图片尺寸大小
如何指定matplotlib输出图片的尺寸? - pythonic生物人的回答 - 知乎 https://www.zhihu.com/question/37221233/answer/2250419008
-
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (12.0, 8.0) -
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,0.5),dpi=300)pool
设置图片分辨率
plt.figure(figsize=(a, b), dpi=dpi)
网格
plt.grid(visible=True,linestyle="--", color='gray', linewidth='1',)
绘制CDF (221211)
Repeat drawing
How to change a matplotlib figure in a different cell in Jupyter Notebook?
|
|
(2022-12-13)
Get the arguments name
use lib inspect with two .f_back:
callers_local_vars = inspect.currentframe().f_back.f_back.f_locals.items().
Getting the name of a variable as a string
Get current color
plt.gca().lines[-1].get_color()
-
use ax Get default line colour cycle
1 2line = ax.plot(x,y) ax.plot(x, y+.3, color = line.get_color())
Combine two figures
Multiple subplots
-
1 2 3 4 5 6 7fig, ax = plt.subplots(3, 3) # draw graph for i in ax: for j in i: j.plot(np.random.randint(0, 5, 5), np.random.randint(0, 5, 5)) plt.show() -
title of subplots:
ax[0][0].set_title("xxx") -
hide x ticks for top subplots and y ticks for right plots: How to set a single, main title above all the subplots with Pyplot?
1 2plt.setp([a.get_xticklabels() for a in axarr[0, :]], visible=False) plt.setp([a.get_yticklabels() for a in axarr[:, 1]], visible=False) -
Set xticks for subplots: How to set xticks in subplots
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=4) # Set the ticks and ticklabels for all axes plt.setp(axes, xticks=[0.1, 0.5, 0.9], xticklabels=['a', 'b', 'c'], yticks=[1, 2, 3]) # Use the pyplot interface to change just one subplot... plt.sca(axes[1, 1]) plt.xticks(range(3), ['A', 'Big', 'Cat'], color='red') fig.tight_layout() plt.show() -
Set the fontsize of numbers of xticks:
plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(), fontsize=12, fontweight="normal", horizontalalignment="left", rotation=90)set_xticks() needs argument for ‘fontsize’ #12318
set_xticklabels-Docs
Scale y-axis
|
|
Composite 2 imgs
(2023-12-20) Setting alpha:
|
|
An example
|
|
3D interactive plot
(2024-03-23)
Make 3D interactive Matplotlib plot in Jupyter Notebook - GfG
-
3D Scatter plot:
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32# for creating a responsive plot %matplotlib widget # importing required libraries from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # creating random dataset xs = [14, 24, 43, 47, 54, 66, 74, 89, 12, 44, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5] ys = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 6, 3, 5, 2, 4, 1, 8, 7, 0, 5] zs = [9, 6, 3, 5, 2, 4, 1, 8, 7, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] # creating figure fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') # creating the plot plot_geeks = ax.scatter(xs, ys, zs, color='green') # setting title and labels ax.set_title("3D plot") ax.set_xlabel('x-axis') ax.set_ylabel('y-axis') ax.set_zlabel('z-axis') # displaying the plot plt.show()
-
3D Bar plot:
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28%matplotlib widget from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np # creating random dataset xs = [2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 6, 2, 1, 7, 2] ys = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] zs = np.zeros(10) dx = np.ones(10) dy = np.ones(10) dz = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] # creating figure figg = plt.figure() ax = figg.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') # creating the plot plot_geeks = ax.bar3d(xs, ys, zs, dx, dy, dz, color='green') # setting title and labels ax.set_title("3D bar plot") ax.set_xlabel('x-axis') ax.set_ylabel('y-axis') ax.set_zlabel('z-axis') plt.show()
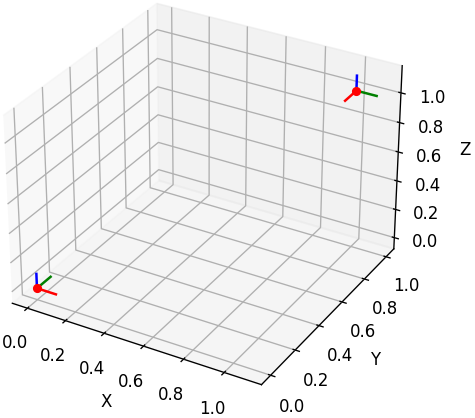
Camera Poses
(2024-03-23)
Generate by ChatGPT with prompt: “How to plot multiple camera poses in a single figure?”
Code
|
|
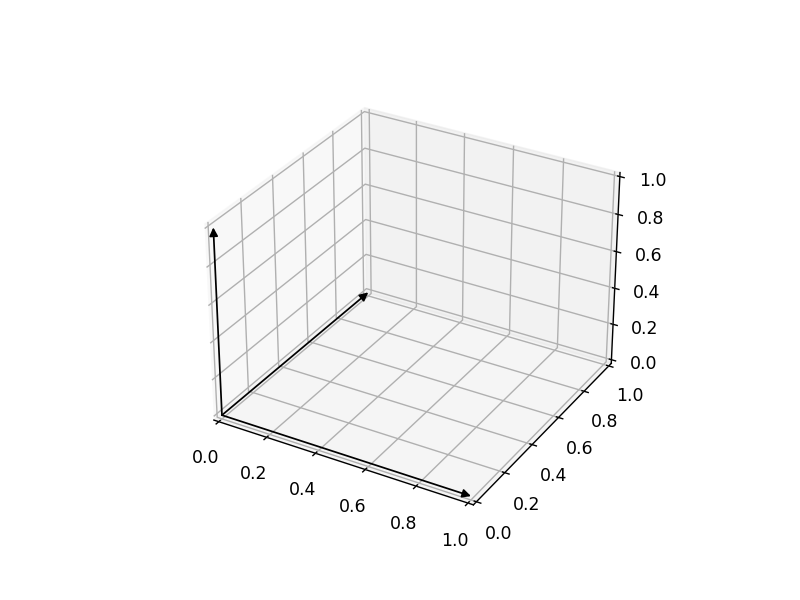
3D arrow
(2024-03-23)
Putting arrowheads on vectors in a 3d plot - SO
Code
|
|
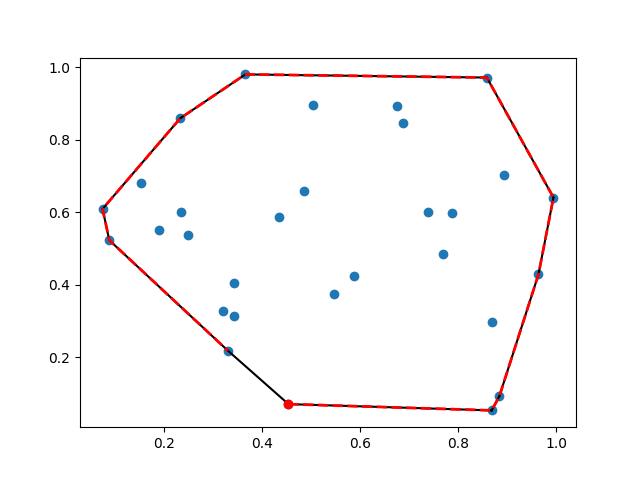
Convex polygon on 2D
(2024-03-26)
How to fill an area within a polygon in Python using matplotlib? - SO
Example from Scipy:
|
|
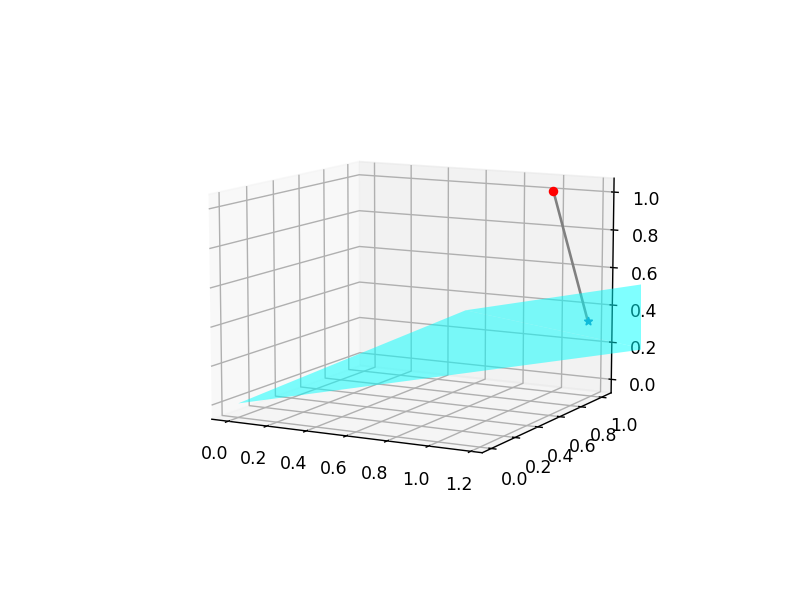
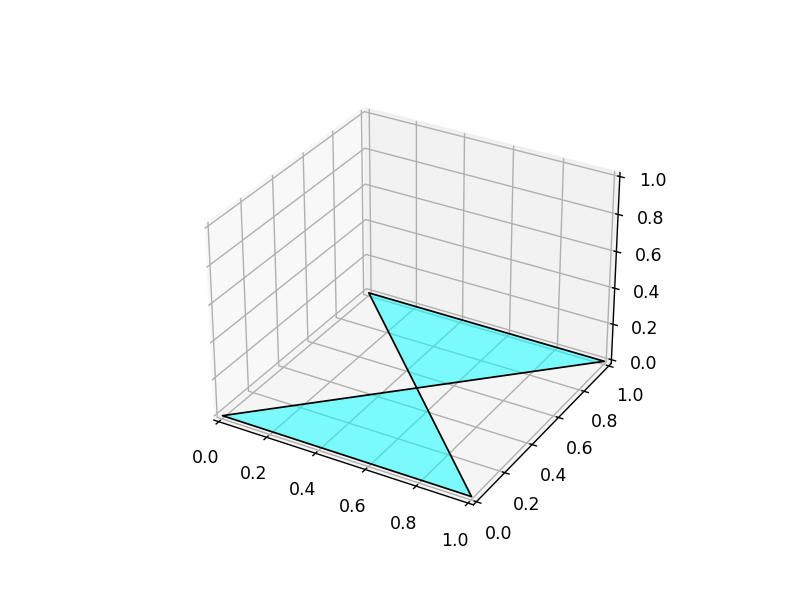
Fill 3D Polygon
(2024-03-26)
ax.fillis used for 2D, and doesn’t work for 3D.
-
ax.add_collection3dcannot follow the counter-clockwise order of convex hull to fill the polygon. For example, when drawing a rectangle, it will fill 2 triangles:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14%matplotlib widget import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d import Poly3DCollection fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') verts = np.array([[ [0,0,0], [1,0,0], [0,1,0], [1,1,0] ]]) # (1,4,3) rec = Poly3DCollection(verts, alpha=0.5, facecolors='cyan', edgecolors='k') ax.add_collection3d(rec)- The
Poly3DCollectioncode is generated by ChatGPT with prompt: “How to fill a 3D triangle with matlabplot”
- The
-
So, I draw 2 triangles to form a quadrilateral:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19%matplotlib widget import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d import Poly3DCollection fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') verts = np.array([[ [0,0,0], [1,0,0], [0,1,0],]]) tri = Poly3DCollection(verts, alpha=0.5, facecolors='cyan',) ax.add_collection3d(tri) verts = np.array([[ [1,0,0], [0,1,0], [1,1,0] ]]) tri = Poly3DCollection(verts, alpha=0.5, facecolors='cyan',) ax.add_collection3d(tri)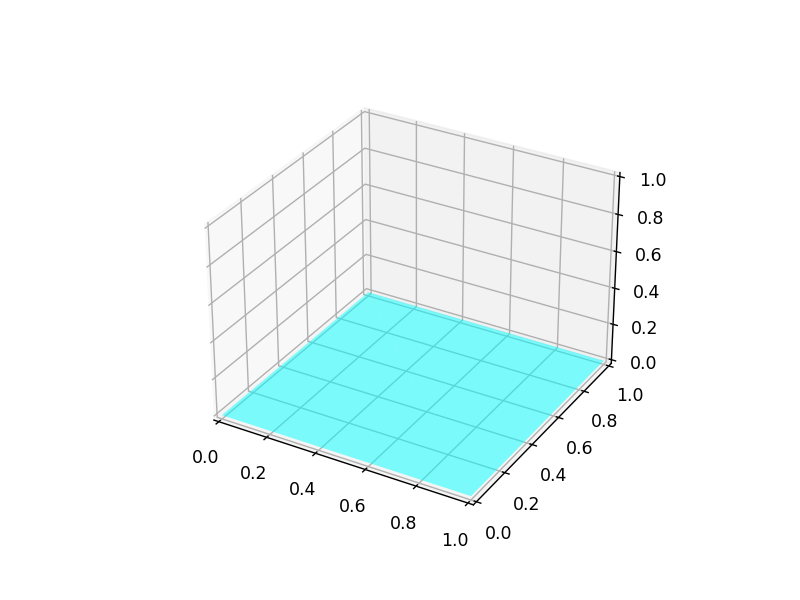
Project 3D point onto plane
(2024-03-26)
How to project a point onto a plane in 3D? - SO
-
The distance from 3D point to the plane: dot product for 3D point and plane normal vector.
-
3D point minus the distance, resulting in the projection.
Code
|
|