Source video: PyTorch Hooks Explained - In-depth Tutorial - Elliot Waite
Hooks for tensor
|
|
This will add a property _backward_hooks for the tensor a.
And hooks for tensors only take effect when back-propagating (when the gradient is calculated).
hook_func can be normal function or a lambda function, which takes as input the gradient grad for this tensor a coming from the last node,
and pass the current gradient to the later backwards graph.
|
|
-
_backward_hooksis an OrderDict so it can contain multiple functions, and they’ll be executed according to their definition sequence.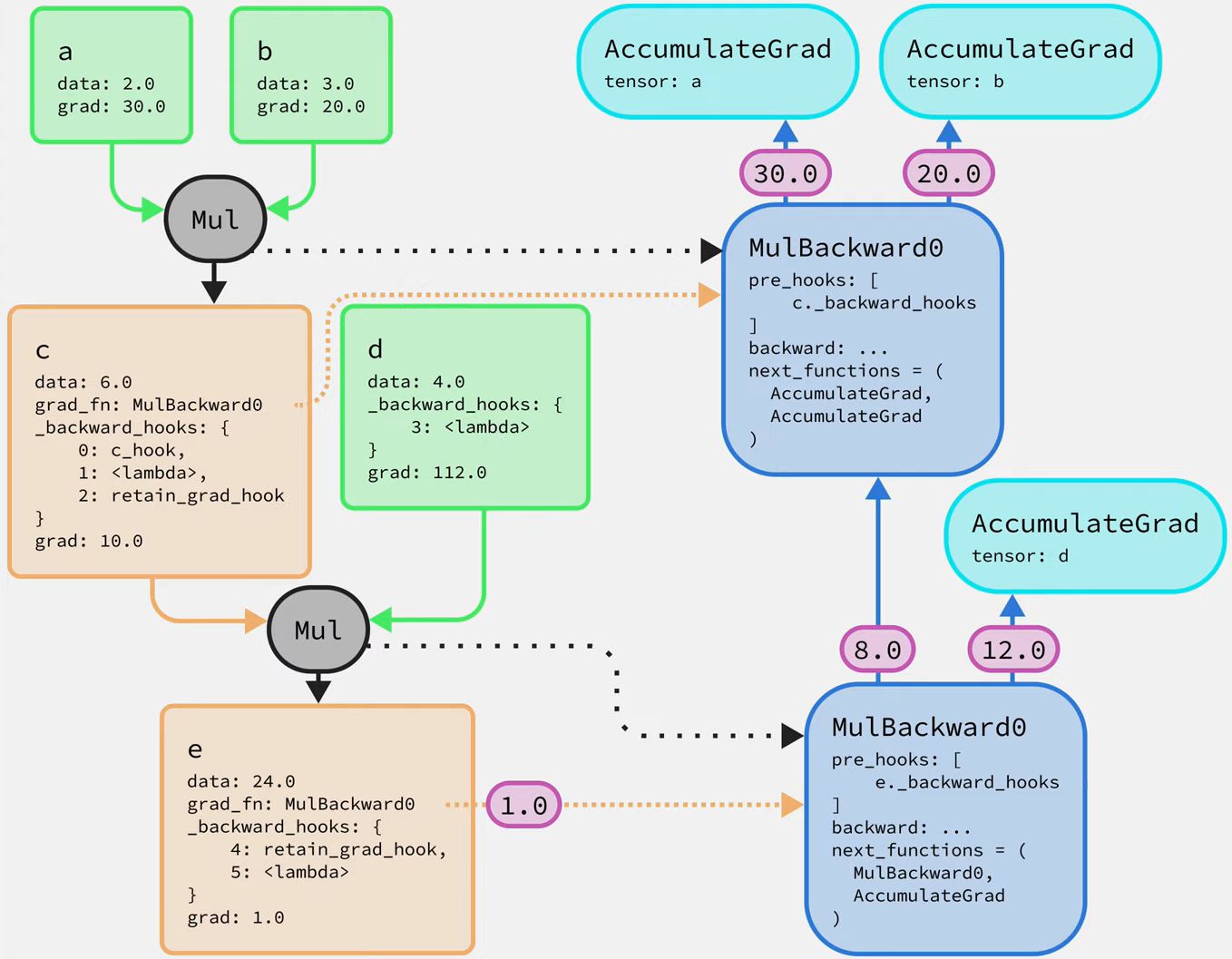
-
Registering a hook for an intermediate node tensor will notify the corresponding tensor in the backwards graph.
Inside the associated node on the backwards graph, there will be an additional property:
pre_hookslist, which will call the hook propertya._backward_hooksof that tensor, before thegradgetting into the methodbackward.So the hook will be executed ahead of
backwardproperty during the back-propagating.backwardwill use the gradients returned from the hooks. -
However, when setting a hook for a leaf node, the hook function will only add the hook func into the
_backward_hooksOrderDict of that leaf node.And the associated
AccumulateGradnode of that leaf node will check if the leaf node has hook function needed to be executed before assigninggradfrom previous calculations. -
Each hook function has a handle index, which will be returned after executing the hook function, e.g.,
h = c.register_hook(hook_func)A hook can be removed via the handle index:h.remove()
Caveat: Change grad in-place in the hook functions may affect other tensors’ gradients, so later backward pass will be mess up.
-
For example, as for the
grad_fnof operatione = c+d, the output gradients for tensorcanddare supposed to be the same. If thegradofdhas changed, thegradofcwill also changed.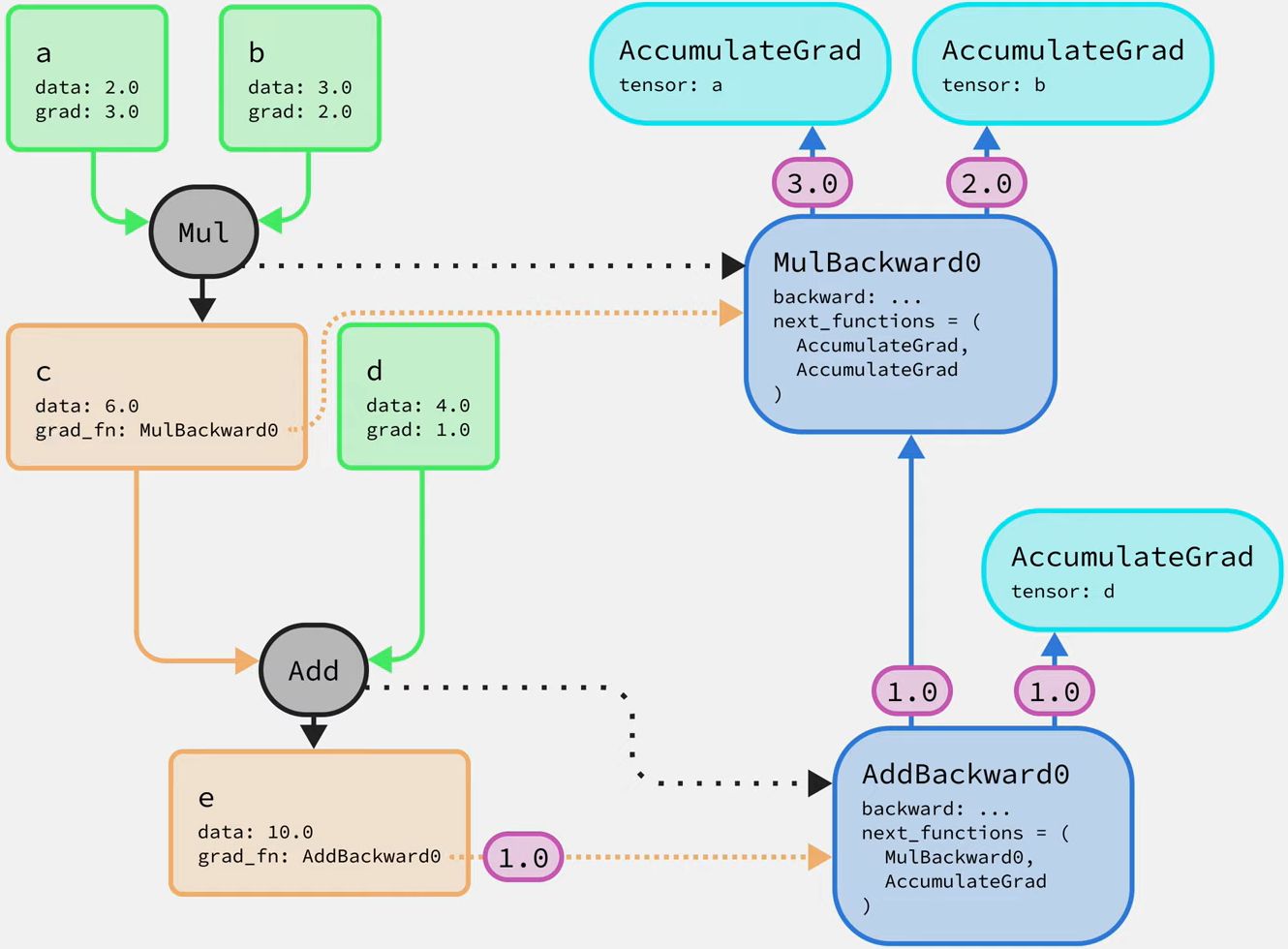
e.g. Gradient clipper ¹
Clamp the gradient of each tensor in a certain range by registering a hook for each parameter.
|
|
Hooks for modules
Hooks registered for modules can be automatically triggered before or after a nn.module.forward is called (even if a layer), so a hook can modify the input and output tensors of a nn.module
-
Hooks before forward
register_forward_pre_hook(hook_func), where thehook_funccan access the module and its positional input.1 2 3 4 5def hook_func_pre_forward(module: nn.Module, inputs: Tensor): a, b = inputs return a+2, b myModel.register_forward_pre_hook(hook_func_pre_forward) -
Hooks after forward:
register_forward_hook(hook_func), where thehook_funcwill recieve 3 arguments: the module, its input, and its output.1 2 3 4def hook_func_forward(module: nn.Module, inputs: Tensor, output: Tensor): return output + 10 myModel.register_forward_hook(hook_func_forward) -
Hooks after backward:
register_backward_hook()has been deprecated in favor ofregister_full_backward_hook()
e.g. Inspect a model ¹
Printing the shape of output tensors after each layer by registering a hook for each layer in an external wrapper,
rather than adding print inside the model.
|
|
e.g. Extract feature maps ¹
|
|