Note
GL_PROJECTION matrix: camera space point(xe,ye,-ze) -> perspective projection to near plane -> homo:(xp,yp,1) -> scale -> homo:(xn,yn,zn,1) -> (x_clip,y_clip,z_clip, w_clip) , where ‘xn,yn,zn’ are variables raning from -1 to 1.
Refer to OpenGL Projection Matrix - songho
Normalized Device Coordinates (NDC) is used to determine whether a 3D point can appear on the computer monitor, which is a cube with length 1. The transformation from eye coordinates to NDC is mapping the truncated pyramid frustum to a cube.
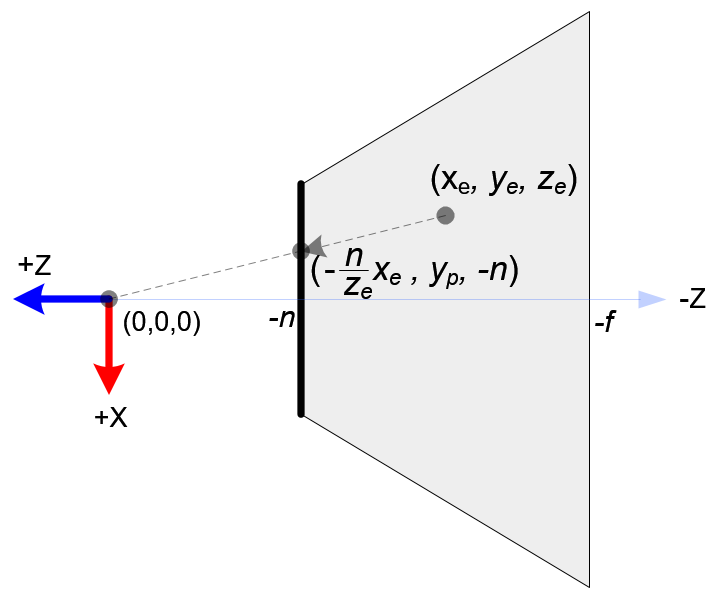
Perspective Projection - songho
According to the perspective projection, the projection point of a world point (xₑ,yₑ,zₑ) on the near plane is
$$ \begin{cases} x_p = \frac{n}{-z_e} x_e \\ y_p = \frac{n}{-z_e} y_e \end{cases} $$
(Camera coordinates is right-hand system looking in the -z direction, while NDC is looking in the z direction under left-hand coordinates)
In order to use a matrix to represent NDC transformation, the homogeneous coordinates are used to enable division, so the transformation can be represented as:
$$ \begin{pmatrix} x_{clip} \\ y_{clip} \\ z_{clip} \\ w_{clip} \end{pmatrix} = M_{projection} \cdot \begin{pmatrix} x_e \\ y_e \\ z_e \\ w_e \end{pmatrix} $$
-
(2024-02-15) wₑ is the homogeneous coordinate for storing the original depth value of the camera point after the multiplication with the projection matrix, where the 4-th row is [0 0 -1 0], so wₑ = 1. And the depth will be divided at the very end step: the perspective division, so as to make the intermediate processes linear operations.
Comparing merely projecting a 3D point onto plane with a
w2c, the projection matrix specifies specific behavior for the z-axis of the ND space (not the source camera space any more).
Therefore, the NDC is:
$$ \begin{pmatrix} x_{ndc} \\ y_{ndc} \\ z_{ndc} \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} x_{clip} / w_{clip} \\ y_{clip}/w_{clip} \\ z_{clip}/w_{clip} \end{pmatrix} $$
Because $w_{clip}$ is the denominator, it should equal to -zₑ; Hence, the forth row of matrix should be $[0\ 0\ -1\ 0]$
Mapping [l, r] and [b, t] to [-1, 1] with linear realtionship: Two points (l,-1),(r,1) can be used to determine the line:
$$ x_{NDC} = \frac{1-(-1)}{r-l} \cdot x_p + β $$
and then substitute (r,1) for $(x_p,x_{NDC})$ to solve β = -(r+l)/(r-l).
Therefore, $x_{NDC} = \frac{2}{r-l}x_p - \frac{r+l}{r-l}$.
Similarly, $y_{NDC} = \frac{2}{t-b} y_p- \frac{t+b}{t-b}$
Substitute xp, yp with the form of xₑ, yₑ:
$$ x_{NDC} = (\frac{2n}{r-l} \cdot x_e + \frac{r+l}{r-l} \cdot z_e) / -z_e \\ y_{NDC} = (\frac{2n}{t-b} \cdot y_e + \frac{t+b}{t-b} \cdot z_e) / -z_e $$
Therefore, the first two row elements of the matrix can be determined.
Suppose the third row is $[0\ 0\ A\ B]$ (z value is independent to x and y), so:
$$ z_{NDC} = \frac{A z_e + B w_e}{-z_e} $$
Substitute the correspondence between (-n, -f) and (-1, 1) into the above equation:
$$ \begin{cases} \frac{-A n + B}{n} = -1 \newline \frac{-A f + B}{f} = 1 \end{cases} $$
Therefore, A = -(f+n)/(f-n), and B = -2fn / (f-n)
Finally, the matrix $M_{projection}$ is
$$ \begin{pmatrix} \frac{2n}{r-l} & 0 & \frac{r+l}{r-l} & 0 \\ 0 & \frac{2n}{t-b} & \frac{t+b}{t-b} & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & \frac{-(f+n)}{f-n} & \frac{-2fn}{f-n} \\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} $$
Code
(2023-10-02)
- 3D world coords multiplied with Inverse intrinsics matrix,
- Scale the [near, far] to [0,1]
Code credits MatchNeRF
|
|
near-far = [0,1]
(2024-01-16)